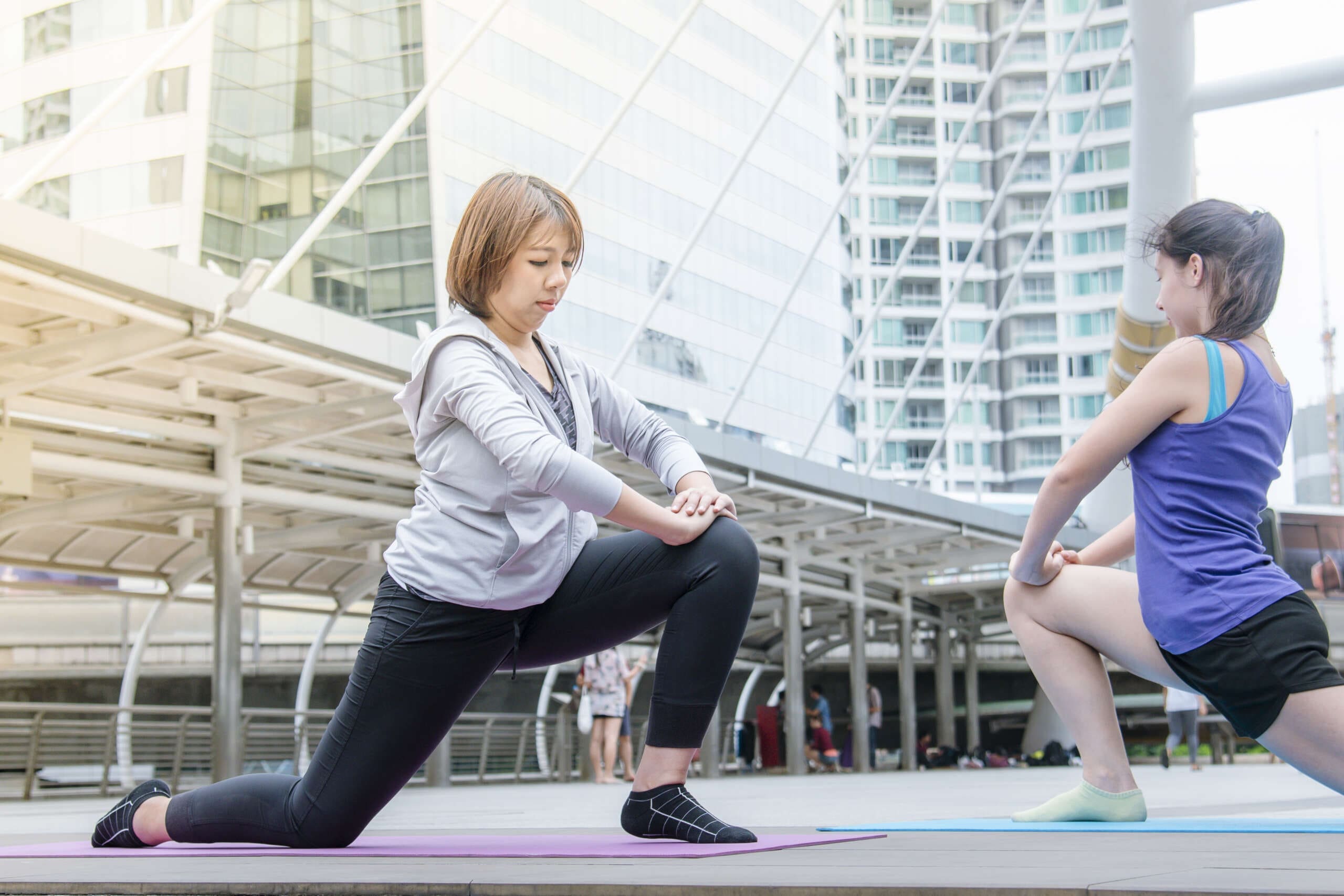
Find out how chiropractic care can support the health of your gluteus medius and contribute to your physical performance.
Table of Contents
Chiropractic Care for Gluteus Medius Injuries and Hip Pain: A Comprehensive Guide
Key Points
- Gluteus Medius Role: The gluteus medius is a key muscle for hip stability and movement, and its dysfunction can lead to hip pain, lower back issues, and knee problems.
- Chiropractic Benefits: Chiropractic care, including spinal adjustments and corrective exercises, can reduce gluteus medius injuries by addressing biomechanical imbalances and promoting natural healing.
- Environmental Factors: Prolonged sitting, poor posture, improper footwear, and repetitive stress contribute to hip pain and gluteus medius weakness, but small lifestyle changes can mitigate these risks.
- Dr. Jimenez’s Expertise: Dr. Alexander Jimenez, a chiropractor and nurse practitioner in El Paso, TX, uses advanced imaging and dual-scope procedures to treat personal injury cases, bridging medical and legal needs.
- Non-Surgical Approach: Combining chiropractic care with exercises, nutrition, and therapies like dry needling can effectively manage hip pain, though individual results may vary.
Understanding Hip Pain and the Gluteus Medius
Hip pain is a common complaint that can turn your daily strut into a limping shuffle, like a zombie in a bad horror flick. At the heart of many hip issues lies the gluteus medius, a muscle that doesn’t get the spotlight it deserves. Located on the outer hip, this fan-shaped powerhouse stabilizes your pelvis, supports your lower back, and keeps your knees from throwing a tantrum during movement. When it’s weak or injured, it’s like your body’s stage manager has quit mid-show, leaving your hips to fend for themselves (Neumann, 2010).
Chiropractic care, as practiced by experts like Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, in El Paso, TX, offers a non-invasive way to address gluteus medius injuries. Unlike popping pills or going under the knife, chiropractic care focuses on restoring balance through adjustments, exercises, and lifestyle tweaks. It’s like giving your hips a stern pep talk to get back in line (El Paso Chiropractor Blog, 2016). Dr. Jimenez’s clinic, Southwest Functional Medicine, also emphasizes nutrition and health coaching to tackle the root causes of pain, making it a holistic haven for those tired of feeling like their hips are plotting against them (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.).
Dr. Jimenez and Personal Injury Cases in El Paso
In El Paso, personal injury cases—think car accidents, slip-and-falls, or workplace mishaps—are no laughing matter, unless your idea of humor is a hospital bill. Dr. Jimenez stands out as a beacon for victims, utilizing advanced imaging techniques (X-rays, MRIs) and diagnostic evaluations to pinpoint injuries such as gluteus medius tears. His unique dual expertise as a chiropractor and nurse practitioner allows him to not only treat patients but also act as a liaison between medical care and legal documentation. This ensures that your injuries are properly recorded for insurance claims or lawsuits, making him the unsung hero of both your hips and your lawyer (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.; Jimenez, n.d.).
Environmental Contributors to Hip Pain
Your hips don’t just start aching because they’re jealous of your knees’ flexibility. Modern life throws a gauntlet of environmental factors at your gluteus medius, from desk jobs to high heels that scream “fashion over function.” Prolonged sitting, poor posture, and repetitive activities can weaken this muscle, leading to pain that feels like your hips are staging a gothic rebellion (Boren et al., 2011). By understanding these factors and making small changes, you can keep your gluteus medius from throwing a tantrum.
Non-Surgical Treatments and Lifestyle Changes
The good news? You don’t need surgery to tame your hip pain. Chiropractic care, combined with therapies such as physical therapy, dry needling, and nutritional coaching, can help strengthen the gluteus medius and alleviate discomfort. Dr. Jimenez’s approach includes personalized plans that incorporate exercises and dietary adjustments, such as swapping processed snacks for anti-inflammatory foods. It’s like telling your hips, “Let’s make peace with some squats and salmon” (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.).
The Gluteus Medius: Your Hip’s Unsung Hero
Anatomy and Function
Picture the gluteus medius as the grumpy gatekeeper of your hip, ensuring everything runs smoothly while muttering about your poor life choices. This muscle originates from the ilium (the upper part of your pelvis) and inserts onto the greater trochanter of the femur. Its primary roles include:
- Pelvic Stability: Keeps your pelvis level during single-leg activities, like walking or climbing stairs.
- Hip Abduction: Enables you to lift your leg sideways, which is essential for movements like stepping out of a car.
- Rotation Support: Assists in internal and external hip rotation, crucial for pivoting or turning.
- Load Distribution: Spreads forces across your joints to prevent overloading your knees or lower back.
When the gluteus medius is weak or injured, it’s like the gatekeeper has fallen asleep, leading to a wobbly pelvis and a condition called Trendelenburg gait, where your hip drops to one side. This can cause pain in the hip, lower back, or even knees, as your body compensates like a poorly choreographed dance (Cooper et al., 2016). Research shows that gluteus medius dysfunction is common in conditions like greater trochanteric pain syndrome (GTPS) and non-specific low back pain, making it a key target for treatment (Grimaldi et al., 2015).
References
- Cooper, N. A., Scavo, K. M., Strickland, K. J., Tipayamongkol, N., Nicholson, J. D., Bewyer, D. C., & Sluka, K. A. (2016). Gluteus Medius Muscle Function in People with and without Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 17(1), 405. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26459494/
- Grimaldi, A., Richardson, C., & Hides, J. (2015). Lateral hip pain: Relation to greater trochanteric pain syndrome. Physical Therapy Reviews, 20(5), 272-280. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34969673/
- Neumann, D. A. (2010). Kinesiology of the musculoskeletal system: Foundations for rehabilitation. Mosby.
How Injuries Occur
Gluteus medius injuries, such as strains or tears, can occur from trauma (e.g., a fall or car accident) or overuse (e.g., running on uneven surfaces). These injuries are like your muscle throwing a dramatic tantrum, refusing to work until you address its grievances. Common causes include:
- Trauma: A sudden impact, like a car crash, can tear the gluteus medius, causing sharp lateral hip pain (Redmond et al., 2018).
- Overuse: Repetitive activities, such as running or cycling with poor form, can strain the muscle, leading to microtears (Grimaldi et al., 2015).
- Weakness: Prolonged inactivity or poor posture can weaken the gluteus medius, making it prone to injury during sudden movements (Boren et al., 2011).
A comprehensive review of hip pain highlights that musculoskeletal issues, including gluteus medius dysfunction, are often linked to both acute injuries and chronic lifestyle factors (Redmond et al., 2018).
References
- Boren, K., Conrey, C., Le Coguic, J., Paprocki, L., Voight, M., & Robinson, T. K. (2011). Electromyographic analysis of gluteus medius and gluteus maximus during rehabilitation exercises. International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy, 6(3), 206-223. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21904698/
- Grimaldi, A., Richardson, C., & Hides, J. (2015). Lateral hip pain: Relation to greater trochanteric pain syndrome. Physical Therapy Reviews, 20(5), 272-280. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34969673/
- Redmond, J. M., Chen, A. W., & Domb, B. G. (2018). Posterior, lateral, and anterior hip pain due to musculoskeletal origin: A narrative literature review of history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, 48(2), 77-87. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29251543/
Environmental Factors Fueling Hip Pain
Your gluteus medius doesn’t just wake up one day and decide to ruin your life—it’s provoked by the modern world’s many insults. Here’s a look at the environmental culprits and how they conspire against your hips:
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Sitting for hours, whether at a desk or binge-watching a series, is like sentencing your gluteus medius to solitary confinement. It weakens the muscle, reducing its ability to stabilize your pelvis (Boren et al., 2011). A study found that prolonged sitting decreases gluteal muscle activation, leading to atrophy and pain (Boren et al., 2011).
- Poor Posture: Slouching or leaning to one side while standing is like asking your hips to carry an uneven load. This stresses the gluteus medius, causing tightness and pain (Ganderton et al., 2017).
- Improper Footwear: High heels or unsupportive shoes alter your gait, forcing the gluteus medius to work overtime. It’s like running a marathon in flip-flops (Grimaldi et al., 2015).
- Repetitive Stress: Activities like running on uneven terrain or cycling with a misaligned saddle can overwork the gluteus medius, leading to inflammation or tears (Redmond et al., 2018).
- Trauma from Accidents: Personal injuries, such as falls or car crashes, can directly damage the gluteus medius, especially in El Paso’s busy environment, where accidents are common (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.).
These factors create a perfect storm for hip pain, but the good news is that they’re modifiable with the right interventions, as Dr. Jimenez’s clinic emphasizes through its holistic approach (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.).
References
- Boren, K., Conrey, C., Le Coguic, J., Paprocki, L., Voight, M., & Robinson, T. K. (2011). Electromyographic analysis of gluteus medius and gluteus maximus during rehabilitation exercises. International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy, 6(3), 206-223. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21904698/
- Ganderton, C., Pizzari, T., Cook, J., & Semciw, A. (2017). A systematic review of rehabilitation exercises to progressively load the gluteus medius. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 26(5), 418-429. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27705082/
- Grimaldi, A., Richardson, C., & Hides, J. (2015). Lateral hip pain: Relation to greater trochanteric pain syndrome. Physical Therapy Reviews, 20(5), 272-280. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34969673/
- Redmond, J. M., Chen, A. W., & Domb, B. G. (2018). Posterior, lateral, and anterior hip pain due to musculoskeletal origin: A narrative literature review of history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, 48(2), 77-87. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29251543/
- Health Coach Clinic. (n.d.). El Paso, TX health coach clinic – Functional medicine and wellness. healthcoach.clinic/
Chiropractic Care: The Clinical Rationale
Chiropractic care is like the Wednesday Addams of healthcare—darkly effective, no-nonsense, and a bit quirky. For gluteus medius injuries, it’s a game-changer because it addresses both the symptoms and the underlying biomechanical issues. Here’s the clinical rationale, backed by science and Dr. Jimenez’s expertise:
Correcting Biomechanical Imbalances
Misalignments in the spine or pelvis can throw your body out of whack, like a gothic mansion with creaky floors. These misalignments increase stress on the gluteus medius, leading to pain or injury. Chiropractic adjustments restore proper alignment, reducing the muscle’s workload and promoting healing (El Paso Chiropractor Blog, 2016). For example, a misaligned pelvis can cause one hip to bear more weight, straining the gluteus medius on that side. Adjustments correct this asymmetry, allowing the muscle to recover.
Strengthening Through Exercises
Chiropractic care doesn’t stop at adjustments. Dr. Jimenez prescribes corrective exercises like side-lying hip abductions, clamshells, or single-leg bridges to strengthen the gluteus medius. A randomized controlled trial found that hip exercises improve physical function and reduce pain in patients with low back pain, which often overlaps with hip issues (Jeong et al., 2020). These exercises are like sending your gluteus medius to boot camp, making it stronger and less likely to sulk.
Soft Tissue Therapies
Techniques like myofascial release or dry needling target trigger points in the gluteus medius, relieving tension and improving blood flow. A clinical trial showed that dry needling and ischemic compression of the gluteus medius reduced pain in patients with non-specific low back pain (Rodriguez-Mansilla et al., 2023). It’s like giving your muscles a massage with a side of acupuncture, minus the candles and soothing music.
Functional Medicine Integration
Dr. Jimenez’s clinic takes a functional medicine approach, addressing systemic factors like inflammation that can exacerbate hip pain. Nutritional coaching, including anti-inflammatory foods (e.g., omega-3s, berries), supports muscle repair and reduces pain (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.). This holistic approach ensures that your body is fighting pain from the inside out, not just masking symptoms.
Diagnostic Precision
Using advanced imaging (X-rays, MRIs) and diagnostic evaluations, Dr. Jimenez identifies the exact cause of gluteus medius pain, whether it’s a tear, strain, or compensatory issue from elsewhere in the body. This precision is crucial for personal injury cases, where accurate documentation can make or break a legal claim (Jimenez, n.d.).
References
- El Paso Chiropractor Blog. (2016, October). Strengthening the gluteus medius after injury. www.elpasochiropractorblog.com/2016/10/strengthening-gluteus-medius-after.html
- Jeong, U. C., Kim, C. Y., Park, Y. H., Hwang-Bo, G., & Nam, C. W. (2020). Core stability and hip exercises improve physical function and activity in patients with non-specific low back pain: A randomized controlled trial. The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine, 251(3), 193-206. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32669487/
- Rodriguez-Mansilla, J., Mejias-Gil, A., Garrido-Ardila, E. M., Jimenez-Palomares, M., Montanero-Fernandez, J., & Gonzalez-Lopez-Arza, M. V. (2023). Effectiveness of dry needling and ischemic trigger point compression in the gluteus medius in patients with non-specific low back pain: A randomized short-term clinical trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(15), 5064. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37568476/
- Health Coach Clinic. (n.d.). El Paso, TX health coach clinic – Functional medicine and wellness. healthcoach.clinic/
- Jimenez, A. (n.d.). LinkedIn profile. www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/
Chiropractic Care for Leg Instability- Video
Non-Surgical Treatments to Complement Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic care is the star of the show, but it’s backed by a talented ensemble of non-surgical treatments that work together to rehabilitate the gluteus medius. Here’s how they contribute:
Physical Therapy
Targeted exercises like resistance band walks, glute bridges, and side-lying leg raises strengthen the gluteus medius, improving its ability to stabilize the pelvis. A systematic review found that progressive loading exercises are effective for rehabilitating this muscle (Ganderton et al., 2017). These exercises are like sending your glutes to the gym with a personal trainer who doesn’t take excuses.
Nutraceuticals and Nutrition
Dr. Jimenez’s clinic emphasizes nutraceuticals—natural supplements like turmeric, fish oil, or collagen—to reduce inflammation and support tissue repair. An anti-inflammatory diet, rich in foods like salmon, walnuts, and leafy greens, complements these efforts (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.). It’s like feeding your hips a gourmet meal instead of fast food.
Health Coaching
Southwest Functional Medicine offers 24/7 health coaching to guide patients in making lifestyle changes, such as improving posture or incorporating daily movement. This personalized support ensures long-term success, like having a life coach who’s obsessed with your hips’ happiness (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.).
Dry Needling
This technique involves inserting thin needles into trigger points in the gluteus medius to release tension and reduce pain. Research supports its efficacy for musculoskeletal pain, especially when combined with other therapies (Rodriguez-Mansilla et al., 2023). It’s like acupuncture with a punk rock edge.
Massage Therapy
Soft tissue massage improves blood flow and flexibility in the gluteus medius, reducing tightness. It’s like giving your muscles a spa day, minus the overpriced smoothies (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.).
Table 1: Non-Surgical Treatments for Gluteus Medius Injuries
| Treatment | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Exercises like glute bridges and resistance band walks to strengthen the muscles | Improves strength, stability, and reduces pain (Ganderton et al., 2017) |
| Nutraceuticals | Natural supplements like turmeric or fish oil can help reduce inflammation | Supports tissue repair and reduces systemic inflammation (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.) |
| Health Coaching | Personalized guidance on lifestyle changes, such as posture and diet | Promotes long-term hip health and pain prevention (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.) |
| Dry Needling | Needles are inserted into trigger points to release tension | Reduces pain and improves muscle function (Rodriguez-Mansilla et al., 2023) |
| Massage Therapy | Soft tissue massage to improve blood flow and flexibility | Relieves tightness and enhances recovery (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.) |
References
- Ganderton, C., Pizzari, T., Cook, J., & Semciw, A. (2017). A systematic review of rehabilitation exercises to progressively load the gluteus medius. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 26(5), 418-429. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27705082/
- Rodriguez-Mansilla, J., Mejias-Gil, A., Garrido-Ardila, E. M., Jimenez-Palomares, M., Montanero-Fernandez, J., & Gonzalez-Lopez-Arza, M. V. (2023). Effectiveness of dry needling and ischemic trigger point compression in the gluteus medius in patients with non-specific low back pain: A randomized short-term clinical trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(15), 5064. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37568476/
- Health Coach Clinic. (n.d.). El Paso, TX health coach clinic – Functional medicine and wellness. healthcoach.clinic/
Dr. Jimenez’s Role in Personal Injury Cases
In El Paso, personal injury cases are as common as tumbleweeds in a desert storm. Whether it’s a car accident, a slip-and-fall, or a workplace injury, hip pain from these incidents often involves the gluteus medius. Dr. Jimenez’s clinic is a lifeline for victims, offering advanced imaging services (X-rays, MRIs) and diagnostic evaluations to confirm injuries, such as tears or strains. His dual expertise as a chiropractor and nurse practitioner allows him to create comprehensive treatment plans while providing detailed medical reports for legal purposes. This ensures that patients recover while their claims are supported with ironclad documentation (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.; Jimenez, n.d.).
For example, a patient with a gluteus medius tear from a car accident might experience lateral hip pain and difficulty walking. Dr. Jimenez uses MRI to confirm the tear, then designs a plan with chiropractic adjustments, corrective exercises, and nutritional support. His reports for legal teams detail the injury’s impact, making him a trusted ally for both healing and justice. It’s like having a doctor who’s part Sherlock Holmes, part healer, and part courtroom advocate (Jimenez, n.d.).
References
- Health Coach Clinic. (n.d.). El Paso, TX health coach clinic – Functional medicine and wellness. healthcoach.clinic/
- Jimenez, A. (n.d.). LinkedIn profile. www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/
Lifestyle Changes to Support Hip Health
Preventing gluteus medius injuries doesn’t require you to become a fitness guru or live like a monk. Small, clinically informed changes can make a big difference. Here are suggestions from Dr. Jimenez’s approach:
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Use an ergonomic chair or standing desk to reduce hip stress during work. Ensure your chair height allows your feet to rest flat, and avoid crossing your legs (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.).
- Daily Movement: Incorporate 10-15 minutes of glute-activation exercises, like side-lying leg raises or glute bridges, into your routine (Ganderton et al., 2017).
- Proper Footwear: Choose shoes with good arch support and cushioning. Save the high heels for special occasions, unless you want your hips to stage a protest (Grimaldi et al., 2015).
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Eat foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (such as salmon and walnuts), antioxidants (like berries and spinach), and limit your intake of processed foods. Dr. Jimenez’s health coaching emphasizes the use of food as medicine (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.).
- Stress Management: Chronic stress tightens muscles, including the gluteus medius. Try yoga or meditation to keep your body relaxed, like a calm before the storm (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.).
Table 2: Lifestyle Changes for Hip Health
| Change | Action | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Ergonomic Adjustments | Use an ergonomic chair or a standing desk | Reduces hip stress and improves posture (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.) |
| Daily Movement | 10-15 minutes of glute-activation exercises | Strengthens gluteus medius, prevents weakness (Ganderton et al., 2017) |
| Proper Footwear | Wear supportive shoes with good cushioning | Improves gait, reduces muscle strain (Grimaldi et al., 2015) |
| Anti-Inflammatory Diet | Eat omega-3s, antioxidants; avoid processed foods | Reduces inflammation, supports recovery (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.) |
| Stress Management | Practice yoga or meditation | Relaxes muscles, reduces tension (Health Coach Clinic, n.d.) |
References
- Ganderton, C., Pizzari, T., Cook, J., & Semciw, A. (2017). A systematic review of rehabilitation exercises to progressively load the gluteus medius. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 26(5), 418-429. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27705082/
- Grimaldi, A., Richardson, C., & Hides, J. (2015). Lateral hip pain: Relation to greater trochanteric pain syndrome. Physical Therapy Reviews, 20(5), 272-280. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34969673/
- Health Coach Clinic. (n.d.). El Paso, TX health coach clinic – Functional medicine and wellness. healthcoach.clinic/
A Dash of Dark Humor
Hip pain is about as fun as attending a funeral in a clown suit. Your gluteus medius, that sulky muscle, might as well be Wednesday Addams, glaring at you for sitting too long and muttering, “I’d rather be in a crypt than deal with your posture.” But fear not—Dr. Jimenez is like the quirky uncle who knows how to charm even the grumpiest muscle back to health. With a few chiropractic adjustments, some targeted exercises, and a sprinkle of nutritional wisdom, your hips will be less like a “haunted mansion” and more like a “functional fortress.” Sure, your gluteus medius might grumble about the extra work, but it’ll thank you when you’re strutting pain-free.
Conclusion
Hip pain and gluteus medius injuries can disrupt your life, but chiropractic care, combined with non-surgical treatments and lifestyle changes, offers a path to recovery. Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s expertise in El Paso, TX, particularly in personal injury cases, ensures that patients receive comprehensive care tailored to their needs. His use of advanced imaging, diagnostic evaluations, and dual-scope procedures bridges the gap between medical treatment and legal documentation, making him a trusted practitioner for those seeking both healing and justice. By addressing biomechanical imbalances, strengthening the gluteus medius, and tackling environmental factors, you can reduce pain and prevent future injuries.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider, such as Dr. Jimenez, for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. The information provided is based on credible sources and clinical insights, but individual outcomes may vary. For professional guidance, contact Southwest Functional Medicine at (915) 412-6677 or visit healthcoach.clinic/.
Key Citations
- Boren, K., Conrey, C., Le Coguic, J., Paprocki, L., Voight, M., & Robinson, T. K. (2011). Electromyographic analysis of gluteus medius and gluteus maximus during rehabilitation exercises. International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy, 6(3), 206-223. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21904698/
- Cooper, N. A., Scavo, K. M., Strickland, K. J., Tipayamongkol, N., Nicholson, J. D., Bewyer, D. C., & Sluka, K. A. (2016). Gluteus Medius Muscle Function in Individuals with and without Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 17(1), 405. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26459494/
- El Paso Chiropractor Blog. (2016, October). Strengthening the gluteus medius after injury. www.elpasochiropractorblog.com/2016/10/strengthening-gluteus-medius-after.html
- Ganderton, C., Pizzari, T., Cook, J., & Semciw, A. (2017). A systematic review of rehabilitation exercises to progressively load the gluteus medius. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 26(5), 418-429. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27705082/
- Grimaldi, A., Richardson, C., & Hides, J. (2015). Lateral hip pain: Relation to greater trochanteric pain syndrome. Physical Therapy Reviews, 20(5), 272-280. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34969673/
- Health Coach Clinic. (n.d.). El Paso, TX health coach clinic – Functional medicine and wellness. healthcoach.clinic/
- Jeong, U. C., Kim, C. Y., Park, Y. H., Hwang-Bo, G., & Nam, C. W. (2020). Core stability and hip exercises improve physical function and activity in patients with non-specific low back pain: A randomized controlled trial. The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine, 251(3), 193-206. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32669487/
- Jimenez, A. (n.d.). LinkedIn profile. www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/
- Neumann, D. A. (2010). Kinesiology of the musculoskeletal system: Foundations for rehabilitation. Mosby.
- Redmond, J. M., Chen, A. W., & Domb, B. G. (2018). Posterior, lateral, and anterior hip pain due to musculoskeletal origin: A narrative literature review of history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, 48(2), 77-87. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29251543/
- Rodriguez-Mansilla, J., Mejias-Gil, A., Garrido-Ardila, E. M., Jimenez-Palomares, M., Montanero-Fernandez, J., & Gonzalez-Lopez-Arza, M. V. (2023). Effectiveness of dry needling and ischemic trigger point compression in the gluteus medius in patients with non-specific low back pain: A randomized short-term clinical trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(15), 5064. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37568476/
Disclaimers
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Chiropractic Care Health Benefits for the Gluteus Medius" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's wellness blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-C) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on dralexjimenez.com, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card