Table of Contents
Introduction
Inside the body, the gut and the intestines make sure that everything is working properly. The gut and intestinal system make sure that the consumed food is being digested and the nutrients from the food are being transported all over the entire body. The gut system makes sure that the body is being supported by regulating the growth, metabolism, and immune support of all the organ systems and that each of the systems is doing its job. When harmful pathogens enter the body and start to disrupt the gut system, it can lead to chronic gut disorders over time if it is not treated right away. In this 2 part series, we will be taking a look at how SIBO and SIFO affect the gut as well as their symptoms. In Part 2, we will be taking a look at different treatments for SIBO and SIFO to optimize gut health. By referring patients to qualified and skilled providers who specialize in gastroenterology services. To that end, and when appropriate, we advise our patients to refer to our associated medical providers based on their examination. We find that education is the key to asking valuable questions to our providers. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
Â
Can my insurance cover it? Yes, it may. If you are uncertain, here is the link to all the insurance providers we cover. If you have any questions, please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900.
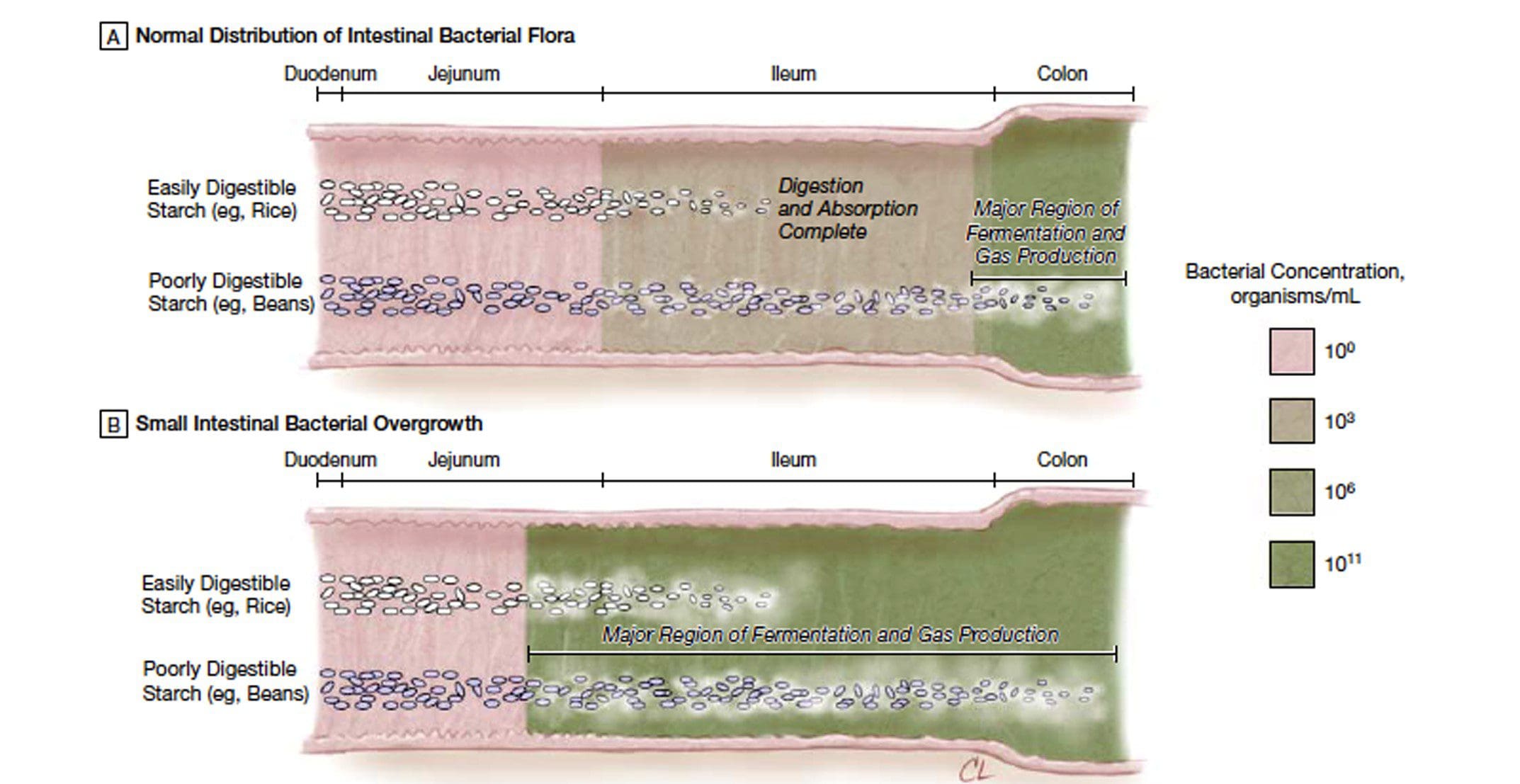
What Is SIBO?
SIBO, or small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, is a condition where an abnormally large number of bacteria (at least 10,000 bacteria per ml of duodenal aspirate) are present in the small intestines. In the small intestines, as research shows, when the food is being digested, gastric acids and biles are being destroyed. The bacteria are being prevented from entering through the intestines, providing optimal function. When there is an abundance of excessive bacteria in the small intestines causing problems, this is known as SIBO. SIBO is a commonly known gastrointestinal disorder that affects millions of individuals. Other research studies have shown that the common risk factors for SIBO include disturbances in the small bowel anatomy and motility in the gut system. The gut system needs the intestines to regulate the good bacteria for the stomach and the other organs to be functional. When SIBO starts to cause the bacterial growth to be excessive, it can cause many gut disorders to pop up and cause many disturbances to the gut and the body.
The Symptoms
The human body requires the balance of beneficial flora in the gut to maintain optimal function of the body through a complex series of chemical and mechanical operations. Research studies show that it is normal to have bacteria living in the intestines. Still, when there is an overabundance of bacteria growing in the intestines, the harmful bacteria can overtake and overwhelm the good bacteria, causing an upset to the digestive system. The harmful bacteria will begin to feed on the consumed food products meant for the good bacteria. Some of the symptoms that are from SIBO include:
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Bloating
- Indigestion
- Constipation
- Unintentional weight loss
- Fatigue
How SIBO Affects The Gut
The small intestines in the gut system ensure that the nutrients and the food mixed with digestive juices are being absorbed into the bloodstream and transported throughout the entire body. When SIBO is developing in the small intestines, research studies have shown that stagnant food in the small intestines is an ideal breeding ground for harmful bacteria to produce toxins and interfere with the absorbed nutrients. SIBO can steal the nutrients from the consumed, digested food. If it is not treated right away, the harmful bacteria will begin to overproduce and take over the beneficial bacteria. This will cause many gut issues and disorders to the gut system causing the body to be dysfunctional.
What Is SIFO?
When there is an abundance of fungal growth in the intestines can lead to many disorders in the gut, just like SIBO. SIFO or small intestinal fungal overgrowth is a condition where abnormally large numbers of fungi/yeast are found in the small bowel that is associated with gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms, as research studies have stated. SIFO is generally defined as greater than 1,000 fungi per ml of small intestinal aspirate that can also occur in the large intestine. This is known as LIFO (large intestinal fungal overgrowth. SIFO and LIFO are commonly used together in clinical settings since it is difficult to ascertain where the overgrowth is. Other research studies have stated that SIFO is usually part of immunodeficiency syndrome with other GI disorders.
The Symptoms
Research studies have found that SIFO can often develop in individuals with either a weakened immune system or a healthy immune system. The Candida species are located in the mouth, the skin, and the intestines. At low levels, it shouldn’t cause any problems in the body or the gut system; however, if it is not being checked, the fungal species will begin to grow uncontrollably, causing various infections in and out of the body. Some of the symptoms that are caused by SIFO are similar to SIBO as they can cause:
- Crohn’s disease
- Ulcerative colitis
- Abdominal bloatingÂ
- Gas
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
Conclusion
The gut system needs beneficial bacteria in the intestines to help digest and absorb nutrients into the bloodstream to be transported throughout the entire body. These beneficial bacteria help maintain the body’s growth, metabolism, and immune support, making it function properly. When harmful pathogens enter the gut system and cause an overabundance of harmful bacteria in the intestines, it can cause the development of both SIBO and SIFO. These gastrointestinal disorders can disrupt the gut system and cause dysfunction in the entire body if it is not treated right away. Incorporating gut-healthy therapies can provide relief to not only the gut but also the body.
References
Achufusi, Ted George O, et al. “Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: Comprehensive Review of Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment Methods.†Cureus, Cureus, 27 June 2020, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7386065/.
Erdogan, Askin, and Satish S C Rao. “Small Intestinal Fungal Overgrowth.†Current Gastroenterology Reports, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Apr. 2015, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25786900/.
Medical Professionals, Cleveland Clinic. “SIBO (Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth): Symptoms, Diet, Causes & What It Is.†Cleveland Clinic, 1 Oct. 2021, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21820-small-intestinal-bacterial-overgrowth-sibo.
Seladi-Schulman, Jill. “SIFO: Small Intestinal Fungal Overgrowth and Your Gut Health.†Healthline, Healthline Media, 4 Dec. 2019, www.healthline.com/health/sifo#what-is-sifo.
Singh, Rajdeep, and Gerard E Mullin. “A Wasting Syndrome and Malnutrition Caused by Small Intestine Fungal Overgrowth: Case Report and Review of the Literature.†Integrative Medicine (Encinitas, Calif.), InnoVision Health Media Inc., June 2017, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6419785/.
Sorathia, Sufian J., et al. “Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth.†StatPearls [Internet]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 31 Jan. 2022, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546634/.
Staff, Mayo Clinic. “Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO).†Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 6 Jan. 2022, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/small-intestinal-bacterial-overgrowth/symptoms-causes/syc-20370168.
Disclaimer
Disclaimers
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "An Understanding Of SIBO & SIFO | Part 1" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's wellness blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-C) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on dralexjimenez.com, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card