Table of Contents
Introduction
Everyone tries to make healthy life choices by boosting their immune system. Getting adequate sleep, eating plenty of fruits and vegetables, drinking plenty of water, and exercising all help increase the immune system. The immune system is known as the “protector” of the body as it eliminates foreign invaders that enter the body and causes chaos to the effective systems. The immune system releases cytokines to the alien invaders causing inflammation in the affected area. When environmental factors affect the body over time, the immune system mistakenly attacks its cells, thinking it’s a foreign invader causing autoimmunity. Today’s article looks at autoimmunity, its triggers, how inflammation plays its role in the body, and what is D.I.R.T. We refer patients to certified providers specializing in autoimmune therapies to help many individuals dealing with autoimmune diseases and inflammation. We also guide our patients by referring to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is the solution to asking our providers insightful questions. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
What Is Autoimmunity?
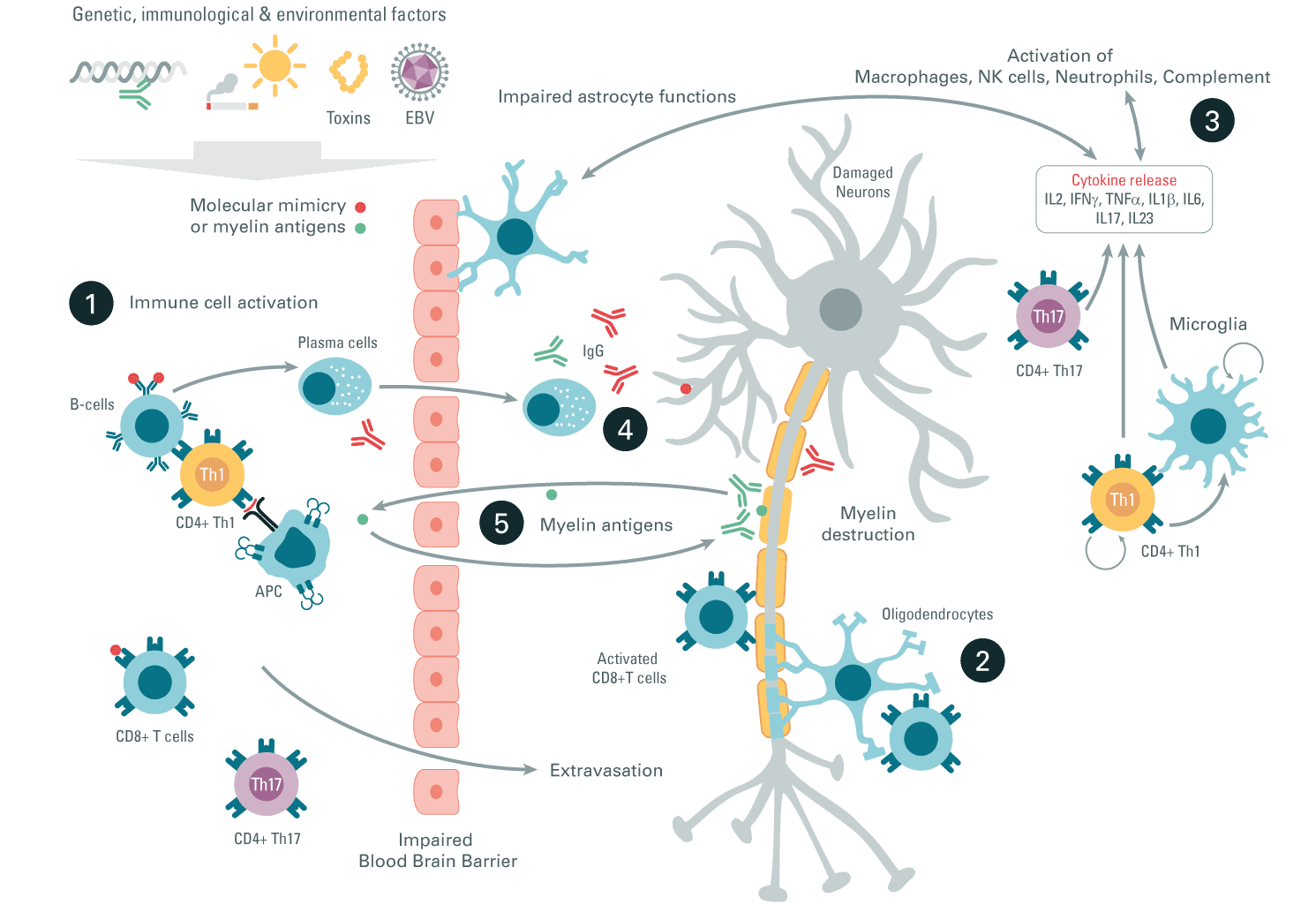
Have you been dealing with abdominal issues that affect you when you eat something? How about pain and swelling in your joints? How about unexplained skin problems? Some of these symptoms are signs that many individuals risk developing autoimmunity. Autoimmunity is defined as a self-directed inflammation of the body’s tissue, which results from a loss of tolerance by aberrant dendric cells and B & T cell responses. This causes the development of immune reactivity towards native antigens. When autoimmune diseases occur in the body, studies reveal that this is due to the immune system attacking self-molecules; many disorders are strongly associated with many predisposing factors.
Things That Trigger Autoimmunity
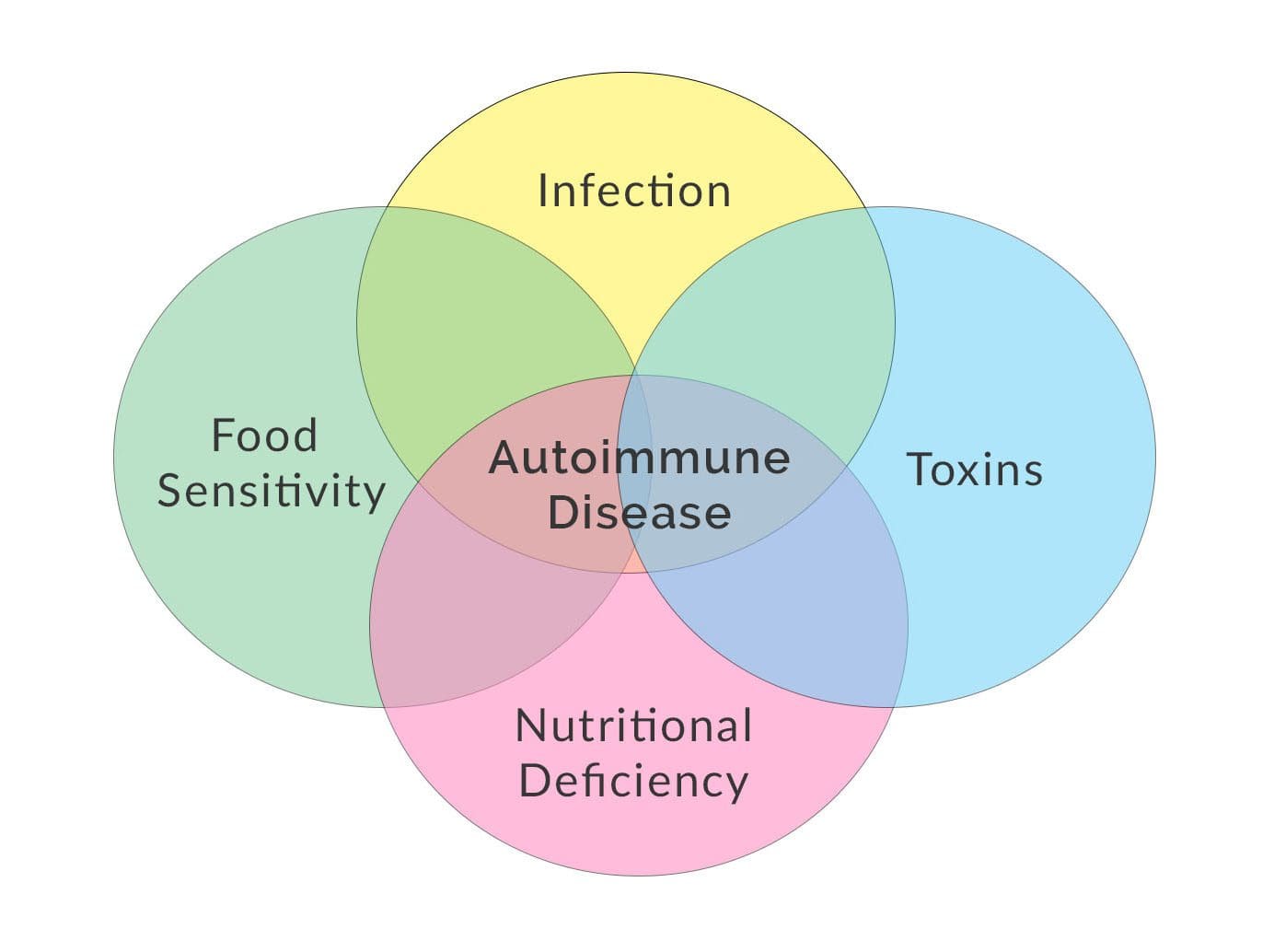
When it comes to the link between the triggering factors and the immune system, studies reveal that the cause and pathway of many autoimmune diseases affecting the body are unknown but that the many factors that trigger the progression of autoimmune diseases are associated with different chronic issues. The adaptive immune response consists of antibodies and activated T lymphocytes that play a predominant role in clinical conditions. The multiple pathways that autoimmune diseases do to the body are ongoing and multifactorial due to the initial trigger for systemic and organ-specific disorders that may predate clinical diseases by many years. Some of the factors that may trigger autoimmunity in the body include:
- Gut
- Endothelial
- Brain
- Stress
- Toxins
- Infections
- Food
- Biotoxins (innate)
What Is Inflammation?-Video
Have you been dealing with swelling around your joints and muscles? Do the foods seem to cause issues in your gut? What about feeling radiating pain traveling down your arms or legs? These are signs that your body is experiencing inflammation. The video above gives an excellent explanation of what inflammation is and its role in the body. Inflammation is the immune system’s natural defenses triggered by various factors that affect the body while it promotes healing to the affected area. Inflammation can be good or bad; it depends on the severity of the body’s injury and location. Inflammation has a casual relationship with the immune system in acute and chronic forms. In its acute form, inflammation can minimize the injury or infection to promote healing in the affected area with heat, redness, and swelling. However, in its chronic condition, where the damage is more profound, various pathogens affecting the body’s tissues may result in chronic issues associated with inflammation. Luckily, there are ways to manage autoimmunity-related inflammatory symptoms.
What Is D.I.R.T?
The body needs the immune system to protect itself from foreign invaders that enter the body. Studies reveal that the immune system does more than protect the body; it can flush out old, damaged cells in the body and replace them with new ones. The immune system also mobilizes responses to the invaders with its ability to distinguish self from non-self. As stated earlier, the immune system has a causal relationship to inflammation. It may succumb to triggering factors that could be involved with the muscles and joints associated with pain. The immune system uses the acronym D.I.R.T. to regulate and defend the body when needed.
D: Detect & Defensive
The immune system in the body has a mechanism that identifies potentially threatening molecular structures like:
- Strange signals found in microbes, food, plants & fungi, chemicals
- Danger signals (alarmins) that are found in tissues or secreted by stimulated leukocytes or epithelia
When these structures attack the body, the immune system begins to detect and becomes a defense mechanism that will mount the appropriate responses to the threat level. Once the threat is eliminated, the body can regenerate new, healthy cells.
I: Internally Regulated
The body has immune responses that are tightly controlled and actively resolved through multiple cellular, genomic, and enzymatic mechanisms. Some of the regulations that the immune system provides are:
- T regulatory lymphocytes
- Lipid-derived pro-resolution mediators
- Redox balance: Nrf2-ARE activation
Even though it is difficult to manipulate the immune system, finding ways to regulate the immune system from going crazy and finding the right balance for a healthy immune system is essential for a healthy body.
R: Restorative
The immune system’s function is to repair any damages resulting from injury or negative encounters that the body has gone through. When the body becomes injured, the immune system sends inflammatory cytokines to the affected area and begins the healing process. Other cellular structures that help the immune system restore the body include:
- Phagocytes
- Fibroblasts
- Stem cells
- Endothelial cells
There are other ways to restore the body and improve the immune system. Eating healthy foods to boost the immune system, exercising, and even getting chiropractic care may help the immune system. But isn’t chiropractic care used for the back? Yes, chiropractic care focuses on the musculoskeletal system, but they also support many individuals in maintaining their health and wellness. The immune system will function to its total capacity when any spinal misalignments or subluxations are corrected through spinal manipulation.
T: Tolerant
The immune system helps the body build a tolerance to the pathogens that are affecting the body. For example, food allergens. With many common food allergens, like nuts, gluten, milk, fish, and eggs, the body will begin to build a tolerance to these allergens when it is introduced slowly. Other healthy boundaries that the immune system provides to the body include:
- Self or fetal antigens
- Innocuous environmental antigens
- Microbes
- Plants and fungi
By building a healthy tolerance to these pathogens, the body has a solid chance to build up immunity to the pathogen. It can help the immune system be stronger when reencountering these pathogens.
Conclusion
Overall the immune system is the primary protector of the body from foreign invaders. When harmful pathogens enter the body, the immune system sends out cytokines to where the invaders are and get rid of them. This causes inflammation in the affected area in the body, causing swelling and redness in the skin. When these pathogens infect the body over time, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body, especially the vital organs causing chronic inflammation associated with autoimmunity. Autoimmunity is a cluster of disorders that causes body dysfunction, which overlaps with inflammation causing the body to be dysfunctional. Luckily it is treatable with the right foods, exercises, and treatments that can help lower inflammation and help regulate the immune system back to its original self.
References
Chaplin, David D. “Overview of the Immune Response.” The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Feb. 2010, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2923430/.
Chen, Linlin, et al. “Inflammatory Responses and Inflammation-Associated Diseases in Organs.” Oncotarget, Impact Journals LLC, 14 Dec. 2017, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5805548/.
Smith, D A, and D R Germolec. “Introduction to Immunology and Autoimmunity.” Environmental Health Perspectives, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Oct. 1999, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1566249/.
Vojdani, Aristo. “A Potential Link between Environmental Triggers and Autoimmunity.” Autoimmune Diseases, Hindawi Publishing Corporation, 12 Feb. 2014, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3945069/.
Disclaimer
Disclaimers
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "How To Manage Inflammatory & Autoimmune Conditions In The Body" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's wellness blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-C) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on dralexjimenez.com, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card