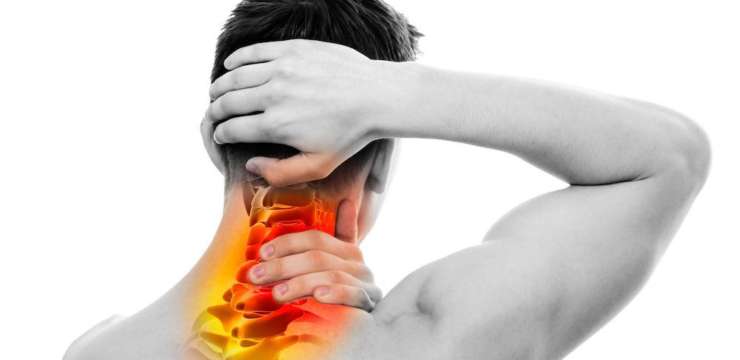
“Those experiencing neck pain, stiffness, headache, shoulder, and back pain may suffer from a whiplash injury. Can knowing whiplash signs and symptoms help individuals recognize the injury and help healthcare providers develop an effective treatment plan?”

Table of Contents
Whiplash Signs and Symptoms
Whiplash is a neck injury that typically occurs after a motor vehicle collision or accident but can happen with any injury that rapidly whips the neck forward and backward. It is a mild to moderate injury of the neck muscles. Common whiplash signs and symptoms include:
- Neck pain
- Neck stiffness
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Shoulder pain
- Back pain
- Tingling sensations in the neck or down the arms. (Johns Hopkins Medicine. 2024)
- Some individuals can develop chronic pain and headaches.
The symptoms and treatment depend on the severity of the injury. Treatment can include over-the-counter pain medicines, ice and heat therapy, chiropractic, physical therapy, and stretching exercises.
Frequent Signs and Symptoms
The sudden whipping movement of the head can affect several structures within the neck. These structures include:
- Muscles
- Bones
- Joints
- Tendons
- Ligaments
- Intervertebral discs
- Blood vessels
- Nerves.
- Any or all of these can be affected by a whiplash injury. (MedlinePlus, 2017)
Statistics
Whiplash is a neck sprain that occurs from a fast neck-jerking motion. Whiplash injuries account for more than half of vehicle traffic collision injuries. (Michele Sterling, 2014) Even with a minor injury, the most frequent symptoms include: (Nobuhiro Tanaka et al., 2018)
- Neck pain
- Next stiffness
- Neck tenderness
- Limited range of motion of the neck
Individuals can develop neck discomfort and pain shortly after an injury; however, the more intense pain and stiffness typically do not occur right after the injury. Symptoms tend to worsen the next day or 24 hours later. (Nobuhiro Tanaka et al., 2018)
Beginning Symptoms
Researchers have found that approximately more than half of individuals with whiplash develop symptoms within six hours of the injury. Around 90% develop symptoms within 24 hours, and 100% develop symptoms within 72 hours. (Nobuhiro Tanaka et al., 2018)
Whiplash vs. Traumatic Cervical Spine Injury
Whiplash describes a mild to moderate neck injury without significant skeletal or neurological symptoms. Significant neck injuries can lead to fractures and dislocations of the spine that can affect the nerves and spinal cord. Once an individual develops neurological problems associated with a neck injury, the diagnosis changes from whiplash to traumatic cervical spine injury. These differences can be confusing as they are on the same spectrum. To better understand the severity of a neck sprain, the Quebec classification system divides neck injury into the following grades (Nobuhiro Tanaka et al., 2018)
Grade 0
- This means there are no neck symptoms or physical examination signs.
Grade 1
- There is neck pain and stiffness.
- Very few findings from the physical examination.
Grade 2
- Indicates neck pain and stiffness
- Neck tenderness
- Decreased mobility or neck range of motion on physical examination.
Grade 3
- Involves muscle pain and stiffness.
- Neurologic symptoms include:
- Numbness
- Tingling
- Weakness in the arms
- Decreased reflexes
Grade 4
- Involves a fracture or dislocation of the bones of the spinal column.
Other Symptoms
Other whiplash signs and symptoms that can be associated with the injury but are less common or only occur with a severe injury include (Nobuhiro Tanaka et al., 2018)
- Tension headache
- Jaw pain
- Sleep problems
- Migraine headache
- Difficulty concentrating
- Reading difficulties
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness
- Driving difficulties
Rare Symptoms
Individuals with severe injuries can develop rare symptoms that often indicate traumatic cervical spine injury and include: (Nobuhiro Tanaka et al., 2018)
- Amnesia
- Tremor
- Voice changes
- Torticollis – painful muscle spasms that keep the head turned to one side.
- Bleeding in the brain
Complications
Most individual generally recover from their symptoms within a few weeks to a few months. (Michele Sterling, 2014) However, whiplash complications can occur, especially with severe grade 3 or grade 4 injuries. The most common complications of a whiplash injury include chronic/long-term pain and headaches. (Michele Sterling, 2014) Traumatic cervical spine injury can affect the spinal cord and be associated with chronic neurological problems, including numbness, weakness, and difficulty walking. (Luc van Den Hauwe et al., 2020)
Treatment
The pain is typically more severe the next day than after the injury. Whiplash musculoskeletal injury treatment depends on whether it is an acute injury or the individual has developed chronic neck pain and stiffness.
- Acute pain can be treated with over-the-counter medicines like Tylenol and Advil, which effectively treat the pain.
- Advil is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory that can be taken with the pain reliever Tylenol, which works in different ways.
- The mainstay of treatment is encouraging regular activity with stretching and exercise. (Michele Sterling, 2014)
- Physical therapy uses various range of motion exercises to strengthen the neck muscles and relieve the pain.
- Chiropractic adjustments and non-surgical decompression can help realign and nourish the spine.
- Acupuncture can cause the body to release natural hormones that provide pain relief, help relax the soft tissues, increase circulation, and reduce inflammation. The cervical spine can return to alignment when the soft tissues are no longer inflamed and spasming. (Tae-Woong Moon et al., 2014)
Neck Injuries
References
Medicine, J. H. (2024). Whiplash Injury. www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/whiplash-injury
MedlinePlus. (2017). Neck Injuries and Disorders. Retrieved from medlineplus.gov/neckinjuriesanddisorders.html#cat_95
Sterling M. (2014). Physiotherapy management of whiplash-associated disorders (WAD). Journal of physiotherapy, 60(1), 5–12. doi.org/10.1016/j.jphys.2013.12.004
Tanaka, N., Atesok, K., Nakanishi, K., Kamei, N., Nakamae, T., Kotaka, S., & Adachi, N. (2018). Pathology and Treatment of Traumatic Cervical Spine Syndrome: Whiplash Injury. Advances in orthopedics, 2018, 4765050. doi.org/10.1155/2018/4765050
van Den Hauwe L, Sundgren PC, Flanders AE. (2020). Spinal Trauma and Spinal Cord Injury (SCI). In: Hodler J, Kubik-Huch RA, von Schulthess GK, editors. Diseases of the Brain, Head and Neck, Spine 2020–2023: Diagnostic Imaging [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2020. Chapter 19. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554330/ doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-38490-6_19
Moon, T. W., Posadzki, P., Choi, T. Y., Park, T. Y., Kim, H. J., Lee, M. S., & Ernst, E. (2014). Acupuncture for treating whiplash associated disorder: a systematic review of randomised clinical trials. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2014, 870271. doi.org/10.1155/2014/870271
Disclaimers
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Whiplash Signs and Symptoms: Explained and Explored" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's wellness blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-C) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on dralexjimenez.com, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card