The function of the SI joints is to allow torsional or twisting movements when moving the legs that act as levers. Without the sacroiliac joints and the pubic symphysis at the front of the pelvis, which allow these precision movements, the pelvis would be at higher risk of a fracture. The sacroiliac joints transmit body weight and all the physical forces down through the sacrum to the hips and legs. Individuals, especially athletes with pain in the lower back, hip, groin, or leg, could be experiencing SIJ/sacroiliac joint dysfunction. A physician or surgeon could recommend sacroiliac joint surgery for severe SI joint dysfunction and pain that has not resolved with conservative treatment.
Table of Contents
 Sacroiliac Joint Surgery
Sacroiliac Joint Surgery
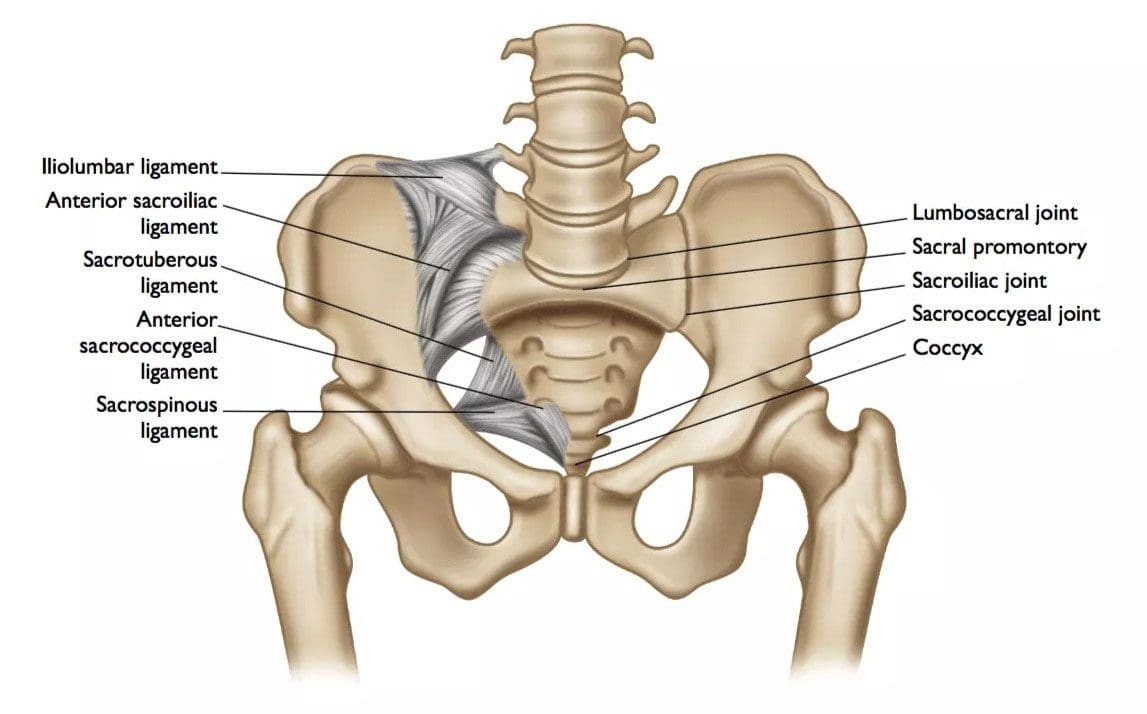
There are two sacroiliac joints. They connect the large iliac bones that make up the sides of the pelvis and the sacrum or triangle-shaped vertebrae between the iliac bones at the base of the spine. Pain in this area can come from sacroiliitis or inflammation of an SI joint, and referred pain may present. A doctor will consider causes such as:
- Trauma
- Sports
- Biomechanical abnormalities
- Wear and tear from weight-bearing stress
- Pregnancy
- Leg length discrepancy
- Hypermobility
- Systemic inflammatory conditions
- Degenerative joint disease
- Scoliosis
- Infection, but this is rare.
Sports
There is a pathology of sacroiliac joint dysfunction in athletes. Sports that require repetitive and/or asymmetric loading that includes:
- Kicking
- Swinging
- Throwing
- Single-leg stance
Any athlete can develop sacroiliac joint dysfunction, but the highest prevalence activities include:
- Soccer
- Football
- Basketball
- Gymnastics
- Golfing
- Powerlifting
- Cross-country skiing
- Step aerobics
- Stair stepper machines
- Elliptical machines
Fusion Surgery
Surgery is not for patients with less than six months of confirmed localized pain or impairment with other causes ruled out. Surgery is the last option for SI joint pain unless it is an emergency. Doctors and surgeons will recommend non-invasive treatment methods before recommending surgery. Surgery recommendations come when the pain has become intolerable, and the individual can no longer move or operate.
- Sacroiliac joint fusion is a minimally invasive procedure involving a small incision less than two inches long.
- Under image guidance, titanium implants are inserted across the sacroiliac joint to provide stability.
- Holes in the hardware allow for adding bone or for the bone to grow naturally across or onto the area to maintain stability.
- This surgery can be either outpatient or overnight, depending on surgeon preference and the type of support available.
Surgery Recovery Time
For most individuals, recovery time is around three weeks on crutches.
- Pain management depends on whether screws or bolts are involved; bolts tend to be more uncomfortable.
- Post-op pain dissipates in a few days or a couple of weeks.
- Fusion itself takes six or more months to complete.
Conservative Treatment Options
Conservative treatment modalities to reduce the inflammation can include:
- Chiropractic
- Physical therapy
- Nonsurgical spinal decompression
- Medications
- Injections
Rest
- Staying off your feet for a few days can help decrease pressure on the SI joint.
- Using an ice or heating pad on the lower back and/or buttocks.
- Massaging the surrounding muscles may help if the apparent cause is an injury.
- A doctor could suggest using a cane, walker, or crutches under medical supervision.
Medications
- Medications include anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or prescription alternatives.
- Acetaminophen helps with pain but not inflammation.
Corticosteroids
- Steroids are the most powerful anti-inflammatory.
- A common nonsurgical treatment is cortisol steroids, injected under X-ray guidance.
- Injections go directly to the source.
- Oral steroids spread throughout the body but can cause undesirable side effects.
Chiropractic and Physical Therapy
- Depending on the severity of the condition, chiropractic and physical therapy may be able to strengthen the muscles around the area and realign the joint.
- A chiropractor will level the pelvis through sacroiliac joint manipulation and mobilization.
Sacroiliac Support Belt
- Wearing a sacroiliac support belt may help remove the joint’s strain and relieve symptoms.
- It works by applying compression around the hip and across the joint.
Back, Hip, and Radiating Pain
References
Brolinson, P Gunnar, et al. “Sacroiliac joint dysfunction in athletes.” Current sports medicine reports vol. 2,1 (2003): 47-56. doi:10.1249/00149619-200302000-00009
Heil, Jessica. “Load-Induced Changes of Inter-Limb Asymmetries in Dynamic Postural Control in Healthy Subjects.” Frontiers in human neuroscience vol. 16 824730. 11 Mar. 2022, doi:10.3389/fnhum.2022.824730
International Journal of Spine Surgery. (2020*) “International Society for the Advancement of Spine Surgery Policy 2020 Update—Minimally Invasive Surgical Sacroiliac Joint Fusion (for Chronic Sacroiliac joint Pain): Coverage Indications, Limitations, and Medical Necessity.” doi.org/10.14444/7156
Peebles, Rebecca DO1; Jonas, Christopher E. DO, FAAFP2. Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction in the Athlete: Diagnosis and Management. Current Sports Medicine Reports: 9/10 2017 – Volume 16 – Issue 5 – p 336-342
doi: 10.1249/JSR.0000000000000410
Disclaimers
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Sacroiliac Joint Surgery: Health Coach Clinic" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's wellness blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-C) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on dralexjimenez.com, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card

 Sacroiliac Joint Surgery
Sacroiliac Joint Surgery