Table of Contents
Introduction
The body has a way to deal with unwanted pathogens that enter the body. The immune system will go and send out the inflammatory cells to the area to deal with the pathogen. Sometimes if the pathogen is still in the body, it can attach to the blood cells and lipids that are traveling throughout the entire body. This can cause chronic issues like metabolic syndrome, metabolic endotoxemia, and even dyslipidemia to the body. In this 2 part series, we will be taking a look at what dyslipidemia is, its symptoms, and how chronic inflammatory macro-and micronutrients can affect the cardiovascular system. Part 2 will be taking a look at what nutraceuticals are used to dampen the effects of dyslipidemia. By referring patients to qualified and skilled providers who specialized in cardiovascular services. To that end, and when appropriate, we advise our patients to refer to our associated medical providers based on their examination. We find that education is the key to asking valuable questions to our providers. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
Can my insurance cover it? Yes, in case you are uncertain here is the link to all the insurance providers we cover. If you have any questions, please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900.
What Is Dyslipidemia?
Dyslipidemia is a condition where the lipid levels in the blood are either too high or too low. Research shows that when there is an imbalance of lipids, which includes cholesterol, LDL-C (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol), triglycerides, and HDL (high-density lipoprotein) are causes the development of atherosclerosis and over time other cardiovascular diseases. The most common underlying reasons for dyslipidemia are:
- Chronic inflammation
- Immune dysfunction
- Oxidative stress of the vascular system
- Poor diet
- Tobacco exposure
- Genetics
- Cardiovascular disease
Even though these are all correct protective/defense mechanisms that can help the body when acute illnesses are affecting the organ systems, they can turn into chronic illnesses over time when unwanted pathogens start to attach themselves to any of the organ systems and cause havoc to the body. Some of the most common reasons for these vascular responses include:
- Chronic inflammatory macro- and micro-nutrient intake.
- Chronic infections (all types including bacteria, virus, fungi, TB, and parasites).
- Toxins, POPs (persistent organic pollutants), and heavy metals.
- Metabolic, inflammatory, immune, toxic, and infectious endotoxemia.
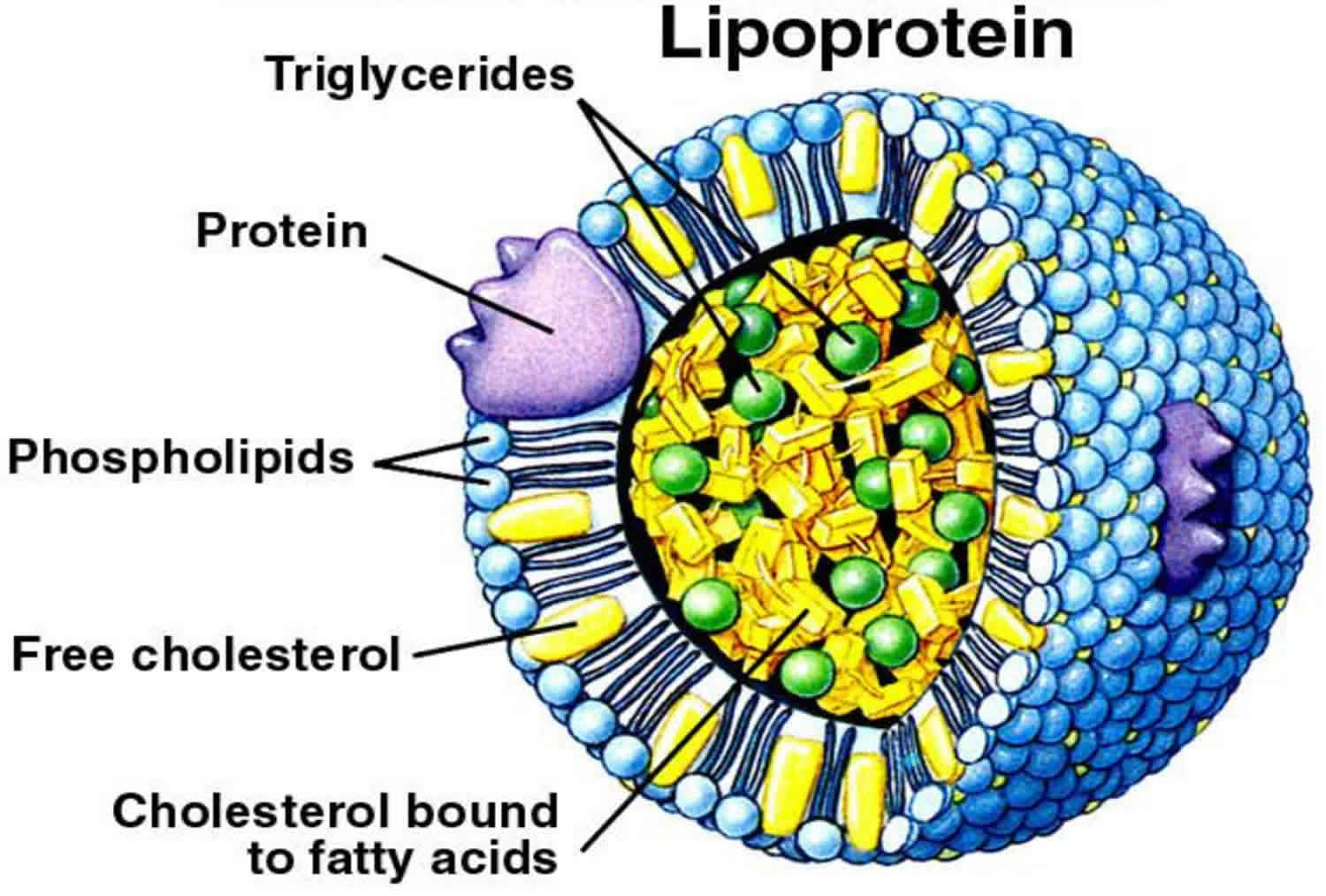
Plasma Lipoproteins Are Important
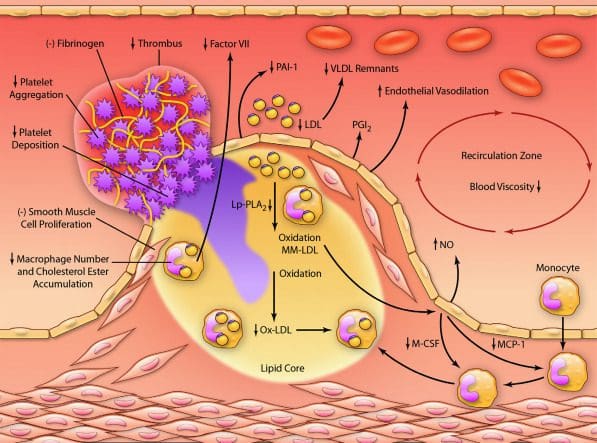
Lipoproteins prevent infections, protect against toxins, and inflammatory nutrition as they are a component of innate immunity. Studies have found that lipoproteins are complex particles in the body that has a central core containing cholesterol esters and triglycerides and plasma lipoproteins can be divided into seven classes based on their lipid composition. Since all lipids and lipoproteins are anti-infective and protect against endotoxin and inflammation-induced vascular damage, they can all detoxify microbial LPS-lipopolysaccharide (gram-negative bacteria) and LTA-lipoteichoic acid (gram-positive bacteria) while binding to LPS to prevent LPS–induced activation of monocytes, macrophages, and pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Other studies have found that plasma lipoproteins are the essential vehicles for lipid distributions for the body’s cellular energy, structural requirements, and excreting out excess lipids out of the body. When there are imbalances in the lipoprotein metabolism that can contribute to metabolic diseases that can range from vascular inflammation to obesity and diabetes. However, as the lipids become modified they become vasculotoxic. The vascular system and heart become “ innocent bystanders†that are injured during the acute, correct defensive/protective responses which will induce atherosclerosis and chronic heart disease.
Dyslipidemia Symptoms
Since cardiovascular disease is involved in the cardiovascular system, dyslipidemia is one of the risk factors that can harm the body. Studies have found that dyslipidemia is considered a metabolic abnormality that can lead to a persistent increase in the plasmatic concentration of cholesterol and triglycerides, being the common cause of morbidity. Other research studies have found that many individuals are unaware that they have dyslipidemia unless it is severe and it is found in a routine blood test. Other symptoms that dyslipidemia can cause in the body include:
- Leg pain
- Chest pain and tightness
- Pain on the neck, jaw, shoulders, and back
- Heart palpitations
- Sleep problems
- Leg swelling
HCTP Therapy
As a form of regenerative medicine, HCTP (human cellular tissue products) or stem cells* are used to help boost the body’s own natural healing process from injuries. Both national and international affiliated clinics and distribution organizations, use HCTP therapy to help repair and regenerate these damaged cells, tissues, and organs back to their original state, so the body can heal faster and the individual can continue on their wellness journey.
Chronic Inflammatory Macro- and Micronutrients
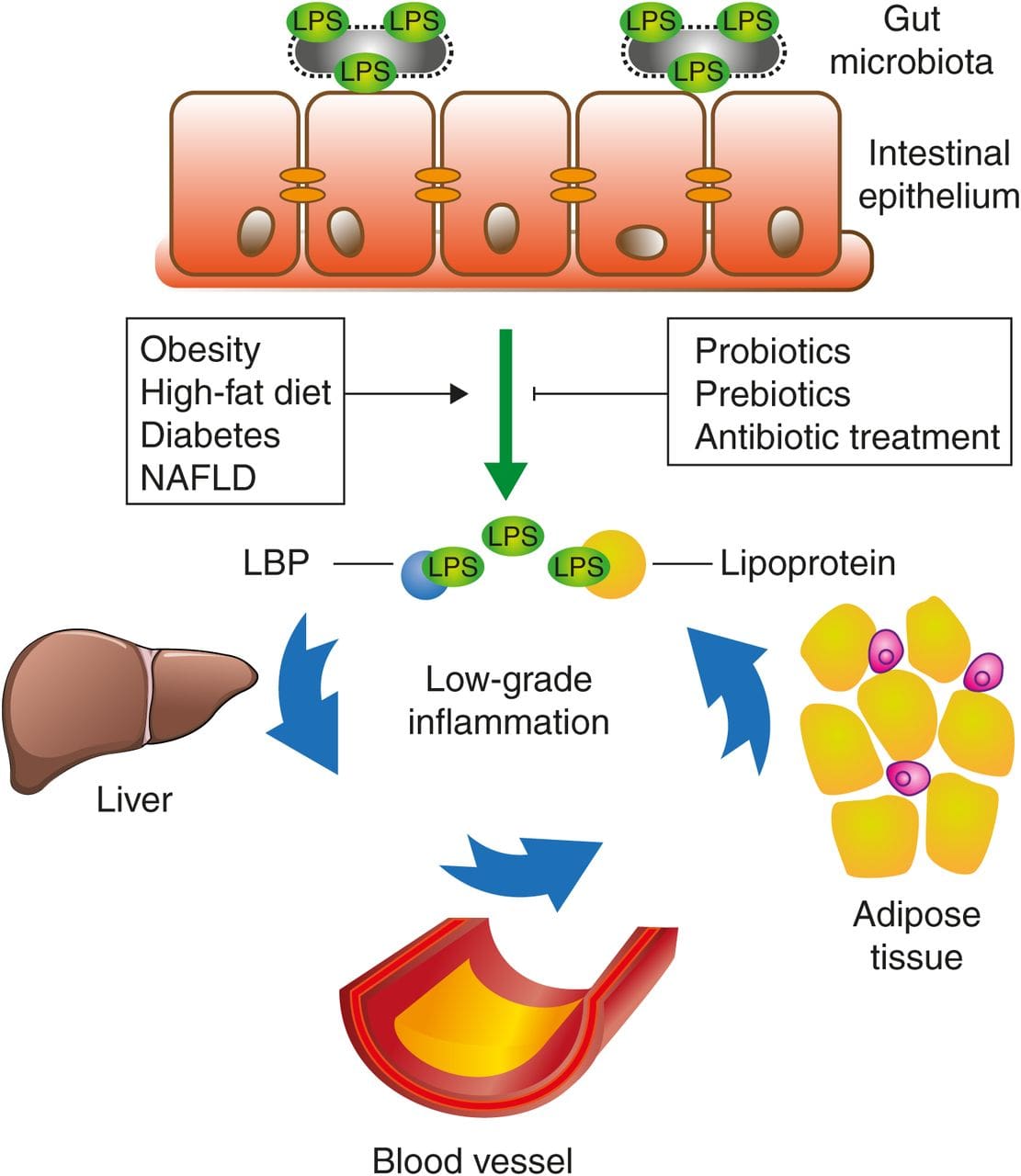
Since the gut plays a role in inflammation and is connected to other organ systems like the brain and the cardiovascular system, it can cause the body to develop chronic inflammation if it is not treated right away. Studies have found that when there are structural changes in the intestinal epithelium that are due to diet alternations can become the results of increasing plasma lipoproteins to induce chronic low-grade inflammation in the body. An inflammatory diet will increase circulating endotoxin levels and with positive correlation with an increase in TC, LDL-C, TG, and decreasing in HDL-C and dysfunctional HDL. This will also correlate with obesity, WC( waist circumference), WHR (waist/hip ratio), insulin levels, IR (insulin resistance), T2 DM, inflammatory cytokines, NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease). When this happens, metabolic endotoxemia will begin to cause a commotion.
Metabolic Endotoxemia & CHD
Research studies show that metabolic endotoxemia is a condition where lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels are elevated despite the presence of any infections that are in the body. Since the gut microbiota signatures (GMS) act as important determinants in the pathogenesis of inflammatory induced obesity, CHD, atherosclerosis, and T2 DM, having metabolic endotoxemia can cause gut dysbiosis and chronic inflammatory diseases that stimulate the innate immune system, TLR4 in adipocytes and vascular tissue, activates NFkB increases inflammation, oxidative stress, and immune dysfunction. While LPS ( lipopolysaccharide) from gram-negative bacteria is the endotoxin from the cell wall that has a high affinity for chylomicrons and cross enterocyte barrier coupled with lipoproteins.
Conclusion
All in all, the body has a way to make sure that no unwanted pathogens attach themselves into the bloodstream and cause chronic issues to cause the body pain. When there are high levels or low levels of lipids that are causing cardiovascular disease risk factors to rise, it can cause the body to be dysfunctional. By incorporating heart-healthy and anti-inflammatory foods and supplements into the body, can provide the necessary nutrients to the body and its organ systems, it can dampen the effects of chronic diseases and the body can begin its recovery process.
References
Ama Moor, Vicky Jocelyne, et al. “Dyslipidemia in Patients with a Cardiovascular Risk and Disease at the University Teaching Hospital of Yaoundé, Cameroon.†International Journal of Vascular Medicine, Hindawi Publishing Corporation, 2017, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5253480/.
Feingold, Kenneth R. “Introduction to Lipids and Lipoproteins.†Endotext [Internet]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 19 Jan. 2021, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK305896/.
Fuke, Nobuo, et al. “Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Endotoxemia with Dietary Factors.†Nutrients, MDPI, 23 Sept. 2019, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6835897/.
Huizen, Jennifer. “Dyslipidemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment.†Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 17 May 2018, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321844.
Li, Kang, et al. “Isolation of Plasma Lipoproteins as a Source of Extracellular RNA.†Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.), U.S. National Library of Medicine, 2018, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6476197/.
Mohammad, Shireen, and Christoph Thiemermann. “Role of Metabolic Endotoxemia in Systemic Inflammation and Potential Interventions.†Frontiers, Frontiers, 11 Jan. 2021, www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2020.594150/full.
Pappan, Nikos, and Anis Rehman. “Dyslipidemia.†StatPearls [Internet]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 15 July 2021, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560891.
Disclaimer
Disclaimers
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "An Integrative Approach To Dyslipidemia | Part 1" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's wellness blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-C) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on dralexjimenez.com, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card