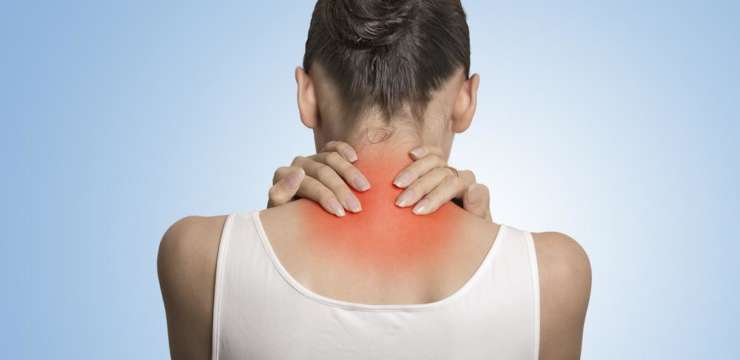
Elbow pain from lifting is a common symptom among individuals who lift weights, heavy objects, children, grocery bags, etc. Depending on the underlying cause, can conservative treatments relieve and heal elbow pain?
Table of Contents
Elbow Pain Caused By Lifting
Elbow pain from lifting can result from weight training, repetitive daily tasks, or job duties like lifting small children or heavy objects. Pain can manifest at the sides or the front of the elbow. Most minor injury cases can be treated with ice, rest, and medications at home. However, pain after lifting can also be a sign of a serious injury, such as a tendon rupture/tear.
Minor Pain From Lifting
Lifting puts pressure on the tendons connecting the wrist and upper arm to the bones in the elbow joint. Minor elbow pain can occur from temporary inflammation in any of these structures after lifting an object. Tendonitis occurs when a tendon becomes inflamed, often from overuse or lifting something too heavy, and ranges from mild to severe. Mild tendonitis typically causes pain during the activity and improves with rest. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2020) Common forms of tendonitis include:
- Tennis elbow – tendonitis on the outside of the elbow
- Golfer’s elbow – tendonitis on the inside of the elbow.
- Biceps tendonitis – at the front of the elbow. (Kheiran A. Pandey, A. & Pandey R. 2021)
Self-Care
Self-care can help reduce elbow pain after lifting and include: (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2020)
Ice
- Add ice to the affected area for up to 20 minutes daily to decrease elbow pain.
Rest
- Avoid lifting heavy objects as much as possible when pain is present.
Wearing A Brace
- If the pain is at the tendons on the inside or outside of your elbow, try wearing a wrist brace to limit the use of your wrist muscles that connect to this area.
Stretching
Gently stretching the wrist flexors and extensors can help reduce elbow pain after lifting. Stretches can be performed several times daily, even after symptoms have resolved. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2024)
- Hold the arm out in front with the palm down. Keep the elbow straight.
- Bend the wrist down so that the fingers are pointing toward the ground.
- With the other hand, gently pull the wrist further down until a stretch is felt along the back of the forearm.
- Hold this position for 15 seconds.
- Repeat five times.
- Next, bend the wrist upward so the fingers point toward the ceiling.
- Using the other hand, gently pull the hand backward until the stretch is felt along the front of the forearm.
- Hold for 15 seconds.
- Repeat five times.
Medication
Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage elbow pain caused from lifting and include: (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2023)
- Advil/Motrin – ibuprofen
- Aleve – naproxen
- Bayer – aspirin
- Tylenol – acetaminophen
Healing
Mild cases can improve after a few days of self-care, whereas more pronounced elbow symptoms can take several weeks, months, or even a year. (Kheiran A. Pandey, A. & Pandey R. 2021) If self-care doesn’t work, physical therapy may be recommended. A physical therapy team can use various modalities and treatments to help reduce pain and inflammation from elbow injuries. The therapy can include targeted exercises to strengthen weak muscles and stretch tight muscles that might contribute to the condition. In addition, the therapy team will help individuals modify their lifting technique to help prevent further injury.
Moderate to Severe Elbow Pain
In addition to sharp, severe pain, serious elbow pain caused from lifting have distinct symptoms, including: (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022)
- Bruising
- Swelling
- Elbow weakness that suddenly happens.
A biceps tendon rupture is a rare but serious injury usually caused from lifting. In addition to other visible signs of the injury, there will be a bulge at the top of the upper arm because the muscle bunches up as it is no longer attached to the elbow. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022) Individuals may hear an audible popping sound if an elbow ligament or tendon gets torn while lifting. (Johns Hopkins Medicine, 2024)
Treatment
Treatment depends on the severity of the injury, but most cases resolve on their own with rest and, if necessary, physical therapy. Conditions that cause severe pain require orthopedic surgeon expertise. These physicians specialize in treating musculoskeletal system injuries. Imaging such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans are often used to determine the extent of damage. Individuals with tendon or ligament tears in the elbow may need surgery to regain full range of motion and strength in their arm. After surgery, physical therapy will help restore function.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other associated medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to improve the body’s flexibility and mobility and resolve musculoskeletal issues.
Shoulder Pain Chiropractic Treatment
References
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2020). Sprains, strains, and other soft-tissue injuries. orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/sprains-strains-and-other-soft-tissue-injuries/
Kheiran, A., Pandey, A., & Pandey, R. (2021). Common tendinopathies around the elbow; what does current evidence say?. Journal of clinical orthopaedics and trauma, 19, 216–223. doi.org/10.1016/j.jcot.2021.05.021
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2024). Therapeutic exercise program for epicondylitis (tennis elbow/golfer’s elbow). orthoinfo.aaos.org/globalassets/pdfs/2024-therapeutic-exercise-program-for-lateral-and-medial-epicondylitis.pdf
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2023). What are NSAIDs? orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/what-are-nsaids/
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2022). Biceps tendon tear at the elbow. orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/biceps-tendon-tear-at-the-elbow
Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2024). Ulnar collateral ligament. www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/ulnar-collateral-ligament-ucl-injuries-of-the-elbow
Disclaimers
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Treating Elbow Pain Caused by Lifting: Effective Methods" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's wellness blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-C) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on dralexjimenez.com, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card