When back pain presents for a prolonged period, the back muscles reduce in mass but increase fat content, resulting in more stiffness. This leads to…


When back pain presents for a prolonged period, the back muscles reduce in mass but increase fat content, resulting in more stiffness. This leads to…

Welcome to our newest functional Medicine presentation, in this episode we will talk Testosterone Deficiency in Men. An expert will help us describe testosterone deficiency,…

Many individuals do not realize the importance of the type of pillow they use for sleep. Sleeping on the wrong pillow is the perfect set-up…

Low back, neck, shoulder, hip, leg, and foot pain causes everyday discomfort and a bad mood. Chronic pain exacerbates the discomfort and bad mood times…

More individuals are reporting extreme levels of stress. Studies indicate that an increasing number of individuals are feeling worried, anxious, or depressed regularly from various…

The quadriceps muscle consists of four muscles in front of the thigh that connects to the knee right below the knee cap. These muscles straighten…

Poor spinal health in adolescence can lead to chronic pain in adulthood. Teenagers, just like adults, can experience back pain from accidents, sports injuries, a…

A non-invasive method of treating scoliosis. Yoga Has Been Shown To Help Reverse Scoliosis. Scoliosis is the lateral curvature of the spine. The spine bends…
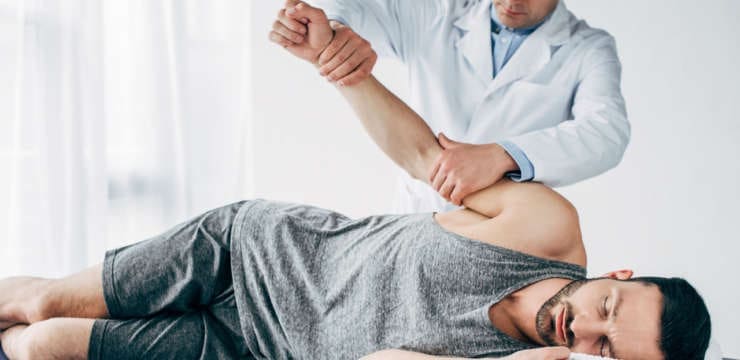
Bursitis types: This is a condition that affects the bursae, which are the small, fluid-filled sacs that provide cushion for the: Muscles Tendons Bones near…
Surgery options when back pain is becoming chronic or so severe that an individual cannot function normally and negatively affects their life. Pretty much everyone…

Individuals and doctors have praised the anti-inflammatory, pain-relieving properties of drinking tea. Inflammation is the body’s natural immune response when injury and infection present. This…

Losing weight can be one of the hardest things to do. It is also one of the best things anyone can do to get rid…

Tennis is a sport that can be enjoyed by individuals of all ages and provides optimal physical activity and cardiovascular exercise. Although it can be leisurely,…

The hands are used for all kinds of tasks/chores day and night. Using the hands requires the wrists. When wrist pain presents, it can make…

There are different possible causes of abdominal pain and digestive problems. Sometimes a bulging disc is the cause. A bulging disc that is causing abdominal…

Studies have found that individuals who consume alcohol in moderation have lower inflammation markers than individuals who do not drink alcohol or heavy drinkers. Other…

Welcome to the last part of our newest functional Medicine presentation brought to you by Dr. Alex Jimenez, in this episode we will talk about…