The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that begin in the cervical/neck spinal cord and travel down the cervicoaxillary canal into the armpit. Forming in the area of the shoulder joint at the branch junction of the brachial plexus, the radial nerve extends down the arm, through the elbow joint, into the forearm, across the wrist, and tips of the fingers. The nerves are susceptible to injury that can cause abnormal function leading to unusual sensations and impaired muscle function.
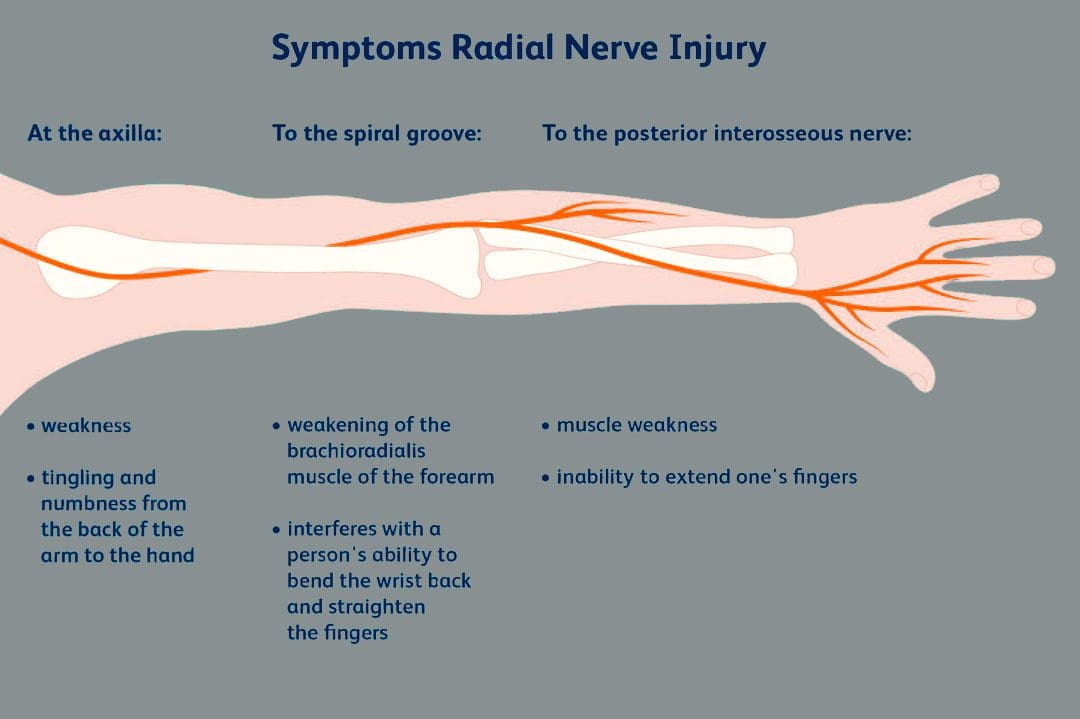
Table of Contents
Radial Nerve
One of the major nerves of the upper extremity.
- There is one brachial plexus on each side of the body that carries the nerves to each arm.
- The radial nerve has two major functions.
- One is to provide sensations in the hands, forearms, arms, and fingers.
- The other is to deliver messages to muscles about when to contract.
Motor Function
- The radial nerve transmits signals to the muscles of the back of the arm and forearm on when to contract.
- Individuals who have abnormal radial nerve function can experience weakness of the muscles and symptoms like wrist drop.
- A wrist drop occurs when the back forearm muscles cannot support the wrist, causing the individual to hold the wrist in a flexed posture.
- Abnormal radial nerve function can cause symptoms of numbness or tingling in the back of the hand.
Conditions
Associated conditions to the radial nerve include lacerations, contusions, fractures, and palsies.
Nerve Contusion
- A contusion typically occurs through blunt force trauma that can crush and smash the nerve area.
- This causes abnormal or no function.
- A nerve contusion can occur from a personal, work, or sports injury or other conditions that generate intense pressure on the nerve/s.
Nerve Lacerations
- A laceration occurs when there is a penetrating injury that cuts and/or severs the nerve.
- This injury can occur from stab wounds or sliced by broken glass, metal, etc.
Fractures
- Broken bones of the upper extremity can lead to extended damage to the nerves near the damaged bone.
- The most common type of fracture associated with radial nerve malfunction is fractures to the humerus bone.
- The nerve wraps tightly around the humerus and can be injured with a fracture.
- Most fracture-related radial nerve injuries heal on their own and do not require surgery.
- However, the way the injury heals can be the difference between normal function and chronic pain.
Crutch Palsy
- Crutch palsy is pressure on the radial nerve in the armpit resulting from using crutches incorrectly.
- To use crutches properly, the individual needs to support their body weight through the hands.
- However, many tend to place pressure around the armpit at the top of the crutch, causing irritation to the nerve in that area.
- Padding the top of crutches and using the proper form can prevent the condition.
Saturday Night Palsy
- Saturday night palsy is the abnormal function of the radial nerve after sleeping in a position that causes direct pressure against the nerve.
- This often occurs when an individual falls asleep with their arm draped over an armrest on a chair.
- The name comes from when individuals are intoxicated and fall asleep in a location other than the bed and in awkward positions.
Treatment
Nerve injuries often cause symptoms at different locations other than where the nerve damage is, complicating diagnosis. Determining the specific location of nerve damage is the first step in developing an appropriate treatment plan. Once the location has been identified, steps can be taken to prevent worsening damage to the nerve.
- The objective is to relieve the pressure from the irritation or compression.
- Chiropractic treatment can relieve symptoms and restore function through:
- Massage to relax the area and increase blood circulation.
- Decompression to physically restore alignment.
- Adjustments to restore body balance.
- Exercises and stretches to maintain treatment, strengthen the muscles, and prevent injuries.
- In cases where there is structural damage, surgery may be necessary to remove pressure or repair damage.
Avoid Surgery
References
Ansari FH, Juergens AL. Saturday Night Palsy. [Updated 2023 Apr 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557520/
Barton, N J. “Radial nerve lesions.” The Hand vol. 5,3 (1973): 200-8. doi:10.1016/0072-968x(73)90029-6
Daly, Michael, and Chris Langhammer. “Radial Nerve Injury in Humeral Shaft Fracture.” The Orthopedic Clinics of North America vol. 53,2 (2022): 145-154. doi:10.1016/j.ocl.2022.01.001
DeCastro A, Keefe P. Wrist Drop. [Updated 2022 Jul 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532993/
Eaton, C J, and G D Lister. “Radial nerve compression.” Hand Clinics vol. 8,2 (1992): 345-57.
Glover NM, Murphy PB. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Radial Nerve. [Updated 2022 Aug 29]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534840/
Ljungquist, Karin L et al. “Radial nerve injuries.” The Journal of hand surgery vol. 40,1 (2015): 166-72. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.05.010
W?giel, Andrzej, et al. “Radial nerve compression: anatomical perspective and clinical consequences.” Neurosurgical review vol. 46,1 53. 13 Feb. 2023, doi:10.1007/s10143-023-01944-2
Disclaimers
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Radial Nerve: Peripheral Upper Extremity" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's wellness blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-C) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on dralexjimenez.com, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
