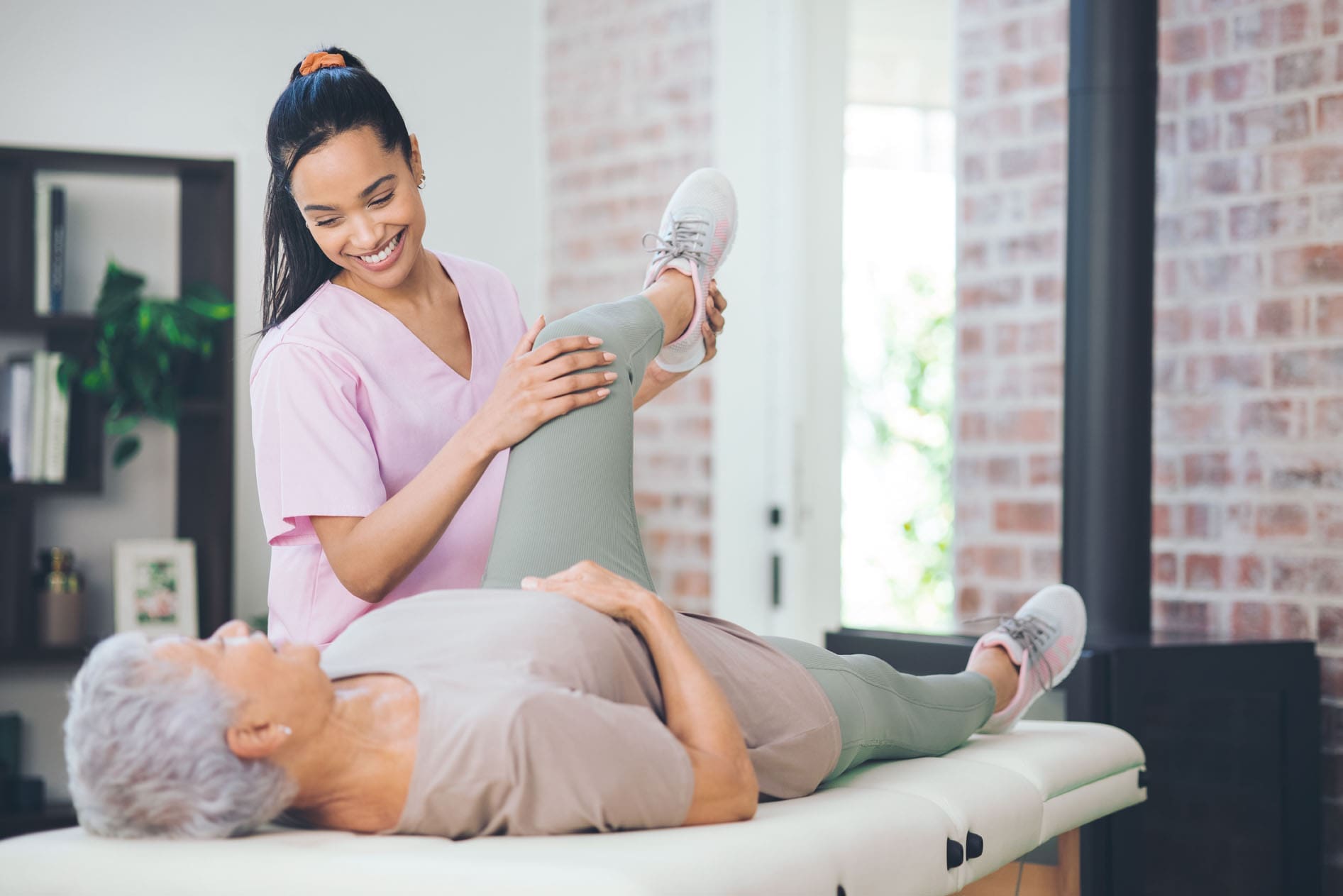
Individuals with hip bursitis often experience discomfort during physical activity, walking, and pain when lying on the affected side. What treatment options are available to control and manage the condition?
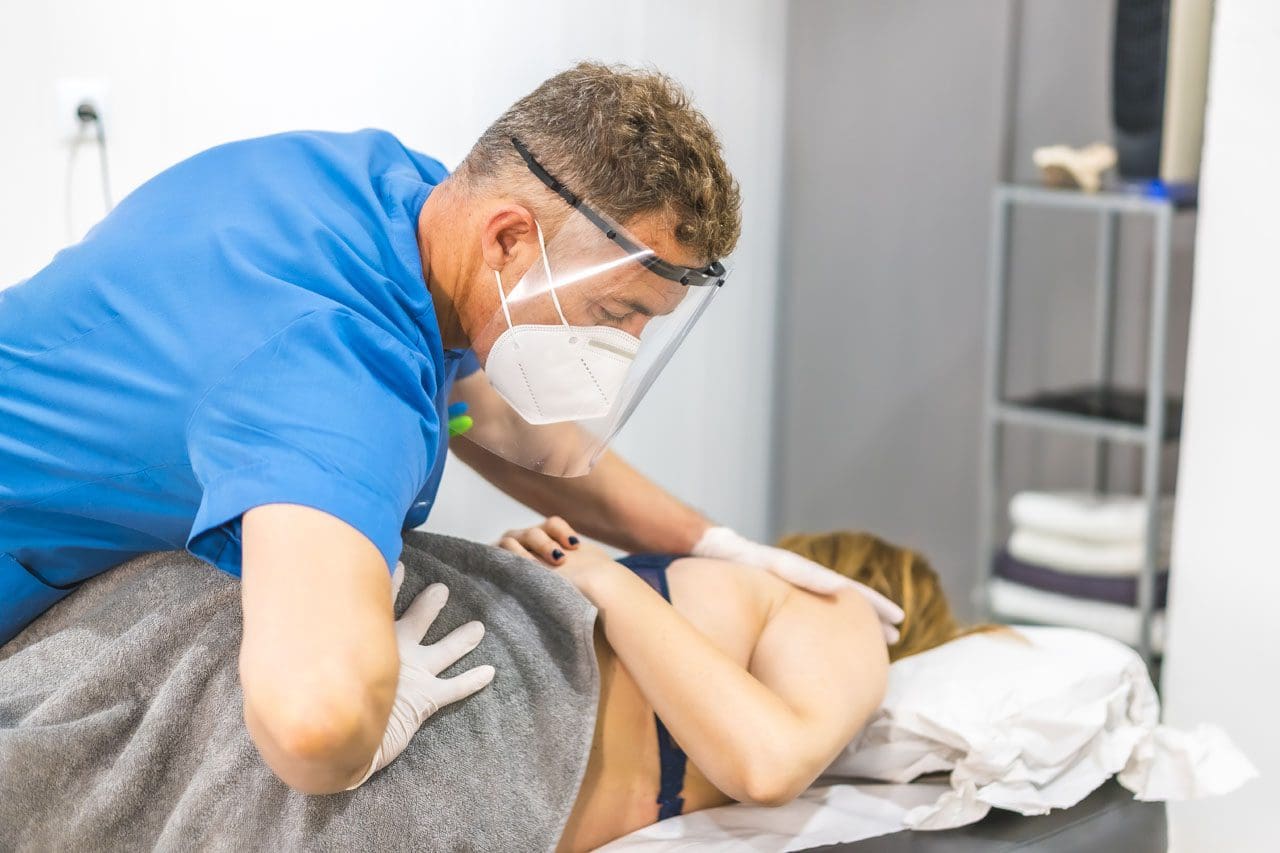
Table of Contents
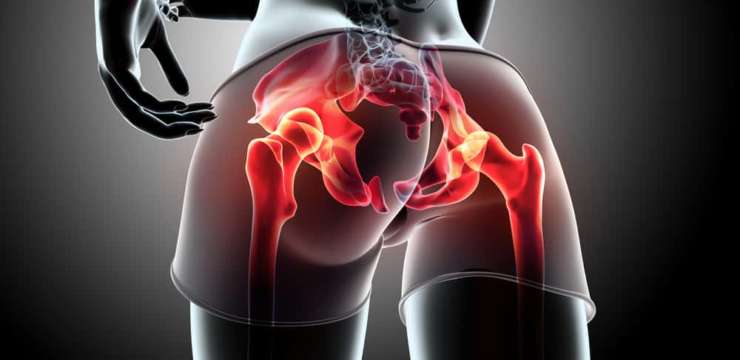
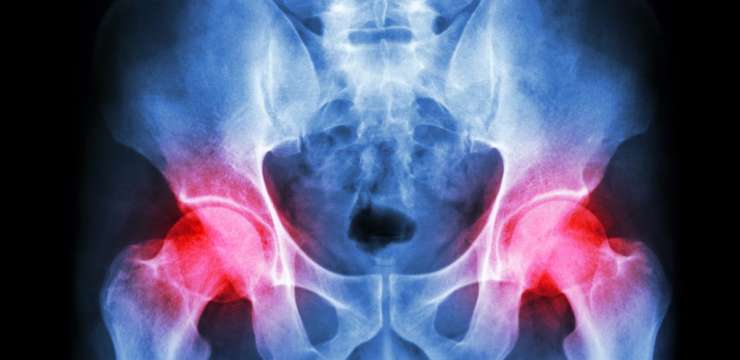
Hip Bursitis
Hip bursitis, also known as trochanteric bursitis, is a common condition that causes pain and discomfort in the hip and upper thigh along the outside of the hip joint. It occurs when one of the hip’s bursae, or fluid-filled sacs cushion joints, becomes inflamed. Treatment for hip bursitis is to control the inflammation caused by this condition.
Causes
Hip bursitis can be caused by injury or overuse of the hip, such as repetitive activities, twisting, or rapid joint movement. It can also be caused by a direct blow or fall to the side of the hip.
Symptoms
- Pain from hip bursitis can be sharp at first and may feel dull and achy later.
- It may be worse when standing up after sitting, moving, or using the hip.
- Individuals may also notice pain when lying on the affected side or sitting for a long time.
Rest
This means a period of not participating in physical, exercise, and sports activities that aggravate symptoms. Any activity that causes hip pain should be avoided as this only contributes to inflammation of the bursa. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022) Modifying how particular activities are performed can help alleviate pressure on the inflamed bursa. Working with a physical therapist can also be recommended. They are experts in movement and alignment, and if certain muscles are overused compared to others, this can lead to unhealthy movement patterns, causing bursa irritation.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Motrin, Aleve, Naprosyn, etc., will help control inflammation (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022). Anti-inflammatory medications can be extremely effective but should be taken cautiously. The instructions on the label need to be followed unless directed otherwise by a healthcare provider. Be aware of side effects and inform the healthcare provider if side effects present.
Cold Therapy
Applying ice to the hip area often helps alleviate the symptoms (National Library of Medicine, 2022). Ice can control inflammation by decreasing blood circulation to the area, especially after physical activity and exercise.
Aspiration
A needle is placed into the bursa to drain the fluid for those with a significant amount of fluid collected within the bursa. (National Library of Medicine, 2022) This is rarely needed in cases of hip bursitis, but when it is done, it can be combined with a cortisone injection.
Cortisone Injections
A cortisone injection may also be given into the bursa to alleviate pain. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022) The cortisone injection is helpful because it can be a diagnostic and therapeutic tool. In cases where hip bursitis may be one of several diagnoses being considered, cortisone can be given to see if it helps alleviate symptoms. Cortisone is a powerful anti-inflammatory medication that can be administered directly to the problem area. These injections are well-tolerated, but there can be possible side effects. Once the initial symptoms are under control, physical therapy strengthening and stretching exercises may be recommended.
Stretching
Most find relief by stretching the muscles and tendons over the outside of the hip, specifically the iliotibial band. The goal is for a better-conditioned muscle and tendon to glide more easily and not cause inflammation. Proper stretching techniques and posture are important in re-injury prevention.
Physical Therapy
Working with a physical therapist is an effective adjunct treatment for bursitis (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022). Physical therapists correct muscle imbalances through stretching and exercise and improve alignment to prevent bursa irritation from reoccurring.
Surgery
Most patients get better with conservative treatment within about six weeks. Surgical treatment for hip bursitis is rarely needed (UCSF Health, 2024). Those who do not rest from their activities until the inflammation subsides often have a return of bursitis symptoms, and those who return too aggressively to activities and do not gradually build up also find that their symptoms return. In cases where surgery is needed, the healthcare provider may recommend an arthroscopic bursectomy. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022) The surgery is an outpatient minimally invasive procedure in which the bursa is removed through a small incision. After a short healing period, the individual can return to normal activity. Crutches may be used for a few days. Common complications are anesthetic-related complications and infection.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
As with any treatment program, always talk with your healthcare provider before initiating specific treatments. Fortunately, treatment of hip bursitis is generally accomplished with conservative therapies. Efforts to limit pressure directly on the bursa, alleviate inflammation, and restore normal movement to the hip joint will typically resolve symptoms. At Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic, we focus on what works for you to relieve pain and restore function. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other associated medical professionals to integrate into a treatment plan to improve the body’s flexibility and mobility, resolve musculoskeletal issues, and prevent future pain symptoms from reoccurring.
The Chiropractic Approach for Pain Relief
References
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2022). Hip bursitis. orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/hip-bursitis
National Library of Medicine. (2022). Bursitis: Learn More – How can bursitis be treated? InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525763/
UCSF Health. (2024). Trochanteric bursitis treatments. www.ucsfhealth.org/conditions/trochanteric-bursitis
Disclaimers
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Hip Bursitis: A Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's wellness blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-C) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on dralexjimenez.com, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card