Table of Contents
Introduction
The endocrine system is where all the hormones are being secreted throughout the entire body. These hormones then travel through the bloodstream to head to their proper locations, whether it is the organs, the brain, the muscles, or the joints, hormones help the body to function normally and that each system is doing its jobs correctly. When there are disruptors or pathogens that can enter the body and affect the hormone levels signal, it can cause a variety of issues and cause the body to develop chronic illness and be dysfunctional. In this 2 part series, we will be taking a look at what are endocrine disruptors and how they affect the body as well as how estrogen is metabolized in the body. Part 2 will be taking a look at estrogen, its two pathways for detoxification, and strategies to detox the body from endocrine disruptors. By referring patients to qualified and skilled providers who specialized in hormone wellness services. To that end, and when appropriate, we advise our patients to refer to our associated medical providers based on their examination. We find that education is the key to asking valuable questions to our providers. Dr. Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
Can my insurance cover it? Yes, in case you are uncertain here is the link to all the insurance providers we cover. If you have any questions, please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900.
What Are Endocrine Disruptors?
An endocrine disruptor is an exogenous substance or mixture that can alter functions of the endocrine system and consequently causes adverse health effects in an intact organism, its progeny, or sub-populations. Studies show that endocrine disruptors are made from both natural and man-made chemicals that can either mimic or even interfere with the body’s hormones. In February 2013, UNEP and WHO released the report State of the Science of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals – 2012 which identifies concerns, including evidence in humans, laboratory animals, and wildlife that exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals can result in adverse effects and highlighted that an important focus should be on reducing exposure to these chemicals.
Since endocrine disruptors can be found in everyday products like plastic bottles, containers, and other items, they are slower to break down when they are in the environment, and over time they can be extremely hazardous causing potential health problems in individuals. With these chemicals or factors, they can cause changes in DNA methylation which not only result in changes in estrogen receptor reactivity but also produce a higher ratio of the 4 and 16 hydroxylated estrogen derivatives that are more genotoxic to the body.
Endocrine Disruptors & Fertility
When the body has been exposed to endocrine disruptors, it can actually affect the fertility rate for both males and females. When endocrine disruptors affect fertility production, the effects on reproduction correlate with altered DNA methylation patterns in the germline. The ability of an environmental factor like endocrine disruptors can reprogram the germline and promote a transgenerational disease state has significant implications for evolutionary biology and disease etiology. Studies show that when females are exposed to endocrine disruptors it can cause infertility, improper hormone production, and menstrual cycle abnormalities. For males, however, studies show that endocrine disruptors can mimic endogenous hormones in the male body causing a low sperm count and potential transgenerational effects.
Another study has found that the exposure of endocrine disruptors on both male and female fertility during the critical preconception period can affect the reproductive hormones and the embryo characteristics. This means that endocrine disruptors can affect both males’ and females’ fertility rates and can affect the embryos.
Endocrine Disruptors & Insulin Resistance
Since insulin resistance is decreased tissue response to the insulin-mediated cellular action, endocrine disruptors can cause an effect on the insulin levels in the body. Studies have found that when there is early exposure to endocrine disruptors, it can cause many metabolic changes that can alter the glucose metabolism and even increased pancreatic secretion and insulin resistance. Other studies even showed that most endocrine can imitate estrogen and beta cells in insulin-sensitive tissues that can generate pregnancy-like metabolic states that are characterized by insulin resistance and even hyperinsulinemia.
The Metabolism of Estrogen
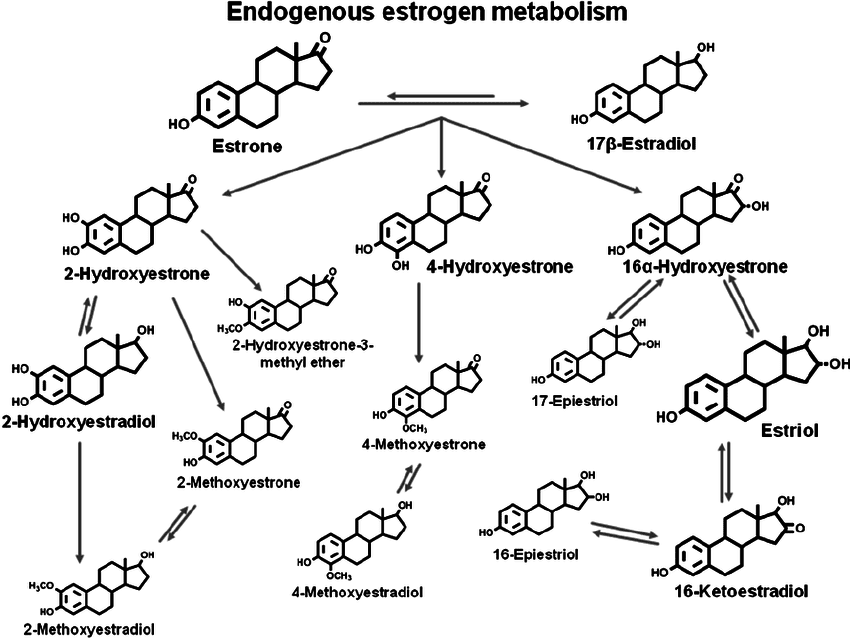
The female body has two hormones that make sure that everything is working properly. There are estrogen and progesterone and these two hormones not only help the reproductive system but also help control the metabolism, heart rate, and puberty. Studies show that when there are unused estrogen hormones in the body, it is metabolized through the liver. It goes through two phases, phase 1 and phase 2 pathways that allow estrogen to be detoxified and excreted from the body. This will allow the 2-OH and the 4-OH estrogen metabolites to go through a further detoxified process known as methylation. Methylation is a form of alkylation with a methyl group that can regulate gene expression and RNA processing for the body. So the hormone estrogen goes through this process so that way the body can function normally and even make sure that the hormone levels are regulated.
Conclusion
All in all, the body needs a functional system to provide the individual with optimal wellness. When there are disruptors that are affecting the body, it can cause unwanted pathogens to enter the body and cause the hormone signals to be dysfunctional. When this happens, the hormone signals can either underproduce or overproduce, causing chronic illnesses to develop over time and cause the individual pain. By changing a person’s lifestyle, the body can begin to heal and regulate the hormone signal properly.
References
Admin, MI. “Science Review: Estrogen Metabolism: Metagenics Institute.†Metagenics Institute | Your Trusted Health, Nutrition, and Personalized Lifestyle Medicine Resource, 14 Jan. 2020, www.metagenicsinstitute.com/ce-education/science-sheets/estrogen-metabolism.
Alonso-Magdalena, Paloma, et al. “Endocrine Disruptors in the Etiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.†Nature Reviews. Endocrinology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 5 Apr. 2011, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21467970/.
Green, Mark P, et al. “Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Impacts on Human Fertility and Fecundity during the Peri-Conception Period.†Environmental Research, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 30 Dec. 2020, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33385395/.
Professionals, NIEHS. “Endocrine Disruptors.†National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 24 Jan. 2022, www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/agents/endocrine/index.cfm.
Rattan, Saniya, et al. “Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors during Adulthood: Consequences for Female Fertility.†The Journal of Endocrinology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, June 2017, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5479690/.
Rotondo, Eleonora, and Francesco Chiarelli. “Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Insulin Resistance in Children.†Biomedicines, MDPI, 28 May 2020, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7344713/.
Sharma, Aditi, et al. “Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Male Reproductive Health.†Reproductive Medicine and Biology, John Wiley and Sons Inc., 14 Apr. 2020, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7360961/.
Disclaimer
Disclaimers
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Detoxifying Strategies For Endocrine Disruptors | Part 1" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's wellness blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-C) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on dralexjimenez.com, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card