
Can performing the hip hinge exercise movement help individuals with lower back pain?
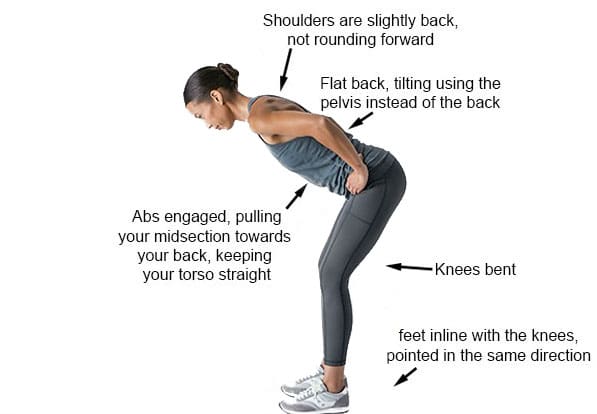
Table of Contents
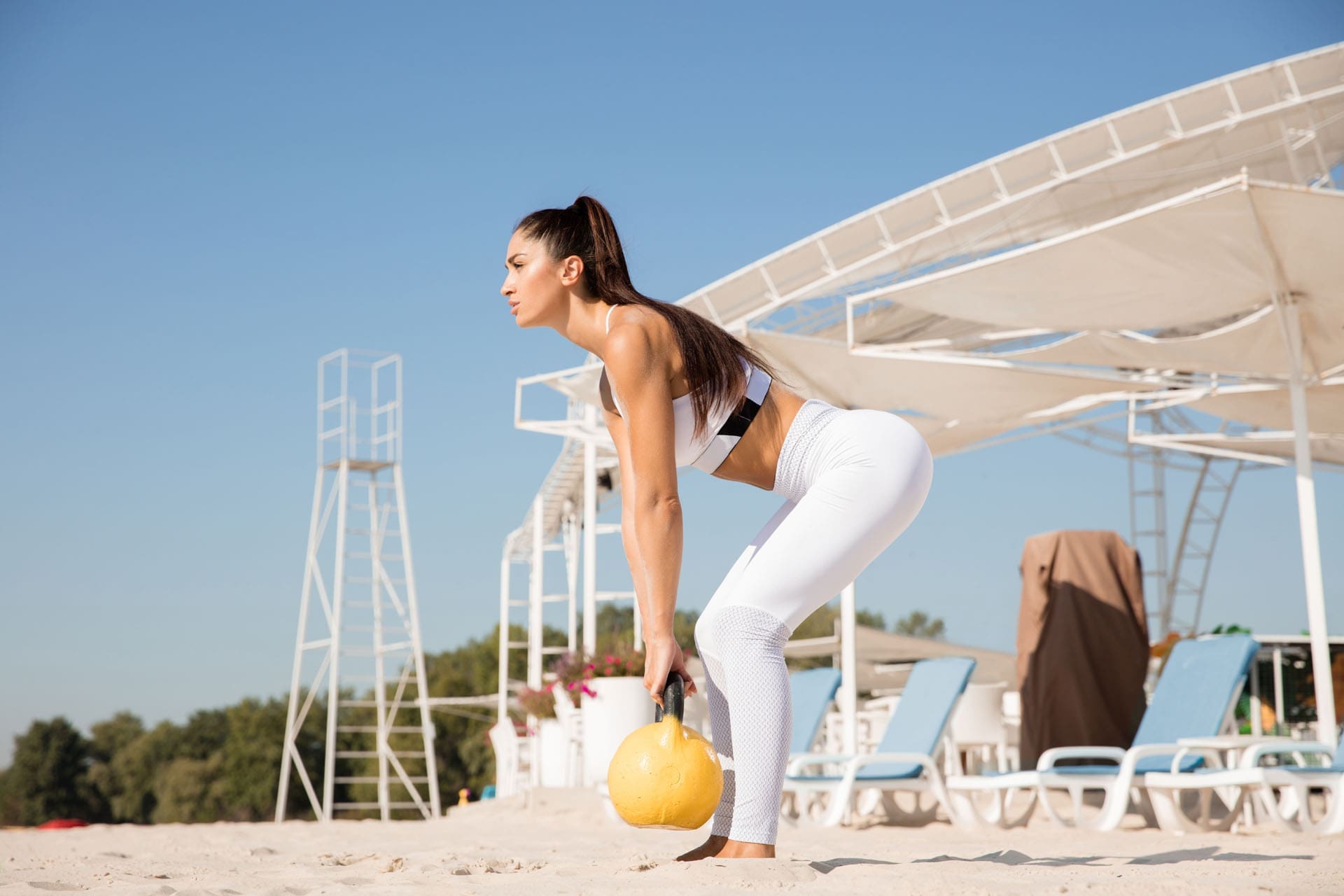
Hip Hinge Exercise
A hip hinge is a controlled movement that involves bending forward from the hips while keeping the spine neutral. The thoracic, lumbar, and pelvis stay neutral while bending forward. The movement comes from the hips, preventing the thoracic and lumbar spine from flexing or rounding. It is a fundamental movement that helps prevent back injuries and strengthens the glutes. It’s used in everyday activities, like picking up objects and sitting down.
The hip hinge exercise targets the posterior chain or back muscles, including the lower back, the glutes, and the hamstrings. It also strengthens the core or abdominal muscles to assist in the movement. When the body hinges at the hips, the bend occurs at the hips, and the spine stays neutral. When the lower back hinges or bends, this causes pain and reduces the range of motion.
Performing the Movement
A wooden dowel, broom handle, or PVC pipe can be used as a guide to help achieve the proper positioning and learn the correct form. Place the dowel or pipe vertically on your back, anchoring it to the head, shoulder blades, and tailbone.
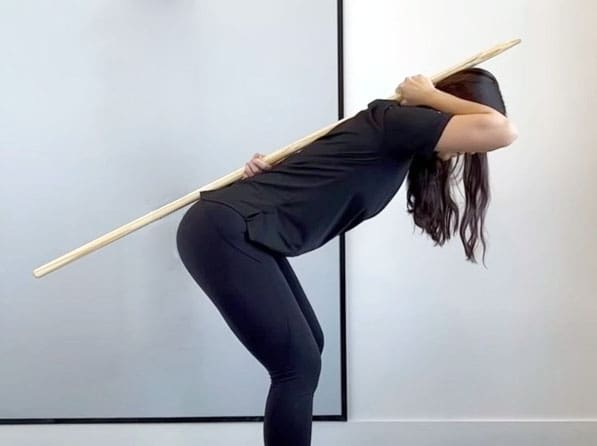

Grasp one end with your right hand in the natural curve of your neck and the other with your left hand in the small of your back. Ensure the dowel touches the back of your head, upper back, and the area where the lower back meets the sacrum. To perform the hip hinge:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart
- Shift your weight to your heels and
- Push your hips back while hinging your torso forward
- Keep your chest open and back flat
- Slightly bend your knees
- Visualize sticking the butt out
- The dowel should not lose contact with the three points as you hinge. If it does, the movement is incorrect.
- Lower your torso until it’s midway between vertical and parallel to the floor.
- Pause when your torso is about 45 degrees
- Keep a slight bend in your knees during the downward and upward phases.
- Reverse the movement by contracting your glutes and pushing your hips forward and upward to return to the starting position.
- Repeat
Benefits
The hip hinge is a fundamental movement pattern that helps the body perform essential tasks such as bending over and picking things up without worry of pain or injury. It’s also required in strength training exercises like the deadlift, kettlebell swing, power clean, and more. The exercise can help strengthen the core, reduce back pain, improve balance, and improve flexion, extension, and trunk rotation. (Michaud F. et al., 2021) Stronger core muscles can increase fitness and athletic performance. (Clark D. R. et al., 2018)
Variations
It is a challenging movement that requires plenty of practice. Individuals who can’t perform it correctly after a few tries may need to modify the movement.
Wall Variation
- Using a wall as a guide is an easy way to make the movement easier.
- To do this, stand with your back to a wall, about three inches away.
- Start hinging at the hips by sticking your butt out touching the wall.
- Keep a neutral spine and a flat back.
Once you can do this several times, try stepping out another inch or two and perform the same modified motion. Stick with this until you are away from the wall and can do a full hinge without the wall.
With A Kettlebell
- Once you master the basic hinge, you can elevate it using a kettlebell to make this move more difficult.
- Start with the kettlebell swing exercise and progress to more challenging moves with the kettlebell.
Common Mistakes
Be aware of common mistakes to keep the move effective and reduce the risk of injury.
Treating the Move Like a Squat
- The hip hinge is not the same as a squat.
- This is a common misconception. When squatting, the knee joint determines the movement pattern.
- But when hip hinging, the movement starts at the hips.
Not Engaging the Core Muscles
- This exercise requires core engagement throughout the entire movement.
- If these muscles relax, there is an increased risk of dipping the hips during the hinge, which can cause the lower back to dip and cause pain.
Using the Lower Back
- Bending or hinging with the lower back rather than letting the hips generate the movement.
- Using the wall as a guide can help reduce and eliminate excessive bending at the waist.
Lost Dowel Contact
- If the dowel loses contact with one or more set-up positions on the back, the hinge is not being executed correctly.
- If your head loses contact with the dowel, the neck is flexing too far forward.
- If you lose contact with the sacrum or lower back area, the spine is flexing too much.
- If you lose contact with the mid-back, the knees are bending rather than the hips.
Safety
Stop and check your form if you feel back pain during any part of the movement. The movement may need to be modified further or decrease how far the hinge is at the hips. If the pain continues, discontinue the exercise and talk with a doctor or a physical therapist before reattempting the exercise. The dowel is a great tool to help maintain a neutral spine. If you cannot perform the hip hinge while keeping the dowel in contact with the body, you might benefit from working with a personal trainer or physical therapist who can walk you through the steps with the correct form.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
Chiropractic care aims to help individuals improve movement with less pain due to condition, after injury, or surgery. A chiropractic physical therapy team can assess your condition and develop a customized treatment plan to expedite pain relief and improve mobility. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to build optimal health and wellness solutions. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, prevent injury, and help mitigate issues through adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal problems.
Chiropractic: The Secret to Unlocking Mobility
References
Michaud, F., Pérez Soto, M., Lugrís, U., & Cuadrado, J. (2021). Lower Back Injury Prevention and Sensitization of Hip Hinge with Neutral Spine Using Wearable Sensors during Lifting Exercises. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 21(16), 5487. doi.org/10.3390/s21165487
Clark, D. R., Lambert, M. I., & Hunter, A. M. (2018). Contemporary perspectives of core stability training for dynamic athletic performance: a survey of athletes, coaches, sports science and sports medicine practitioners. Sports medicine – open, 4(1), 32. doi.org/10.1186/s40798-018-0150-3
Disclaimers
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "The Importance of the Hip Hinge for Injury Prevention and Strength" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's wellness blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-C) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on dralexjimenez.com, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card






