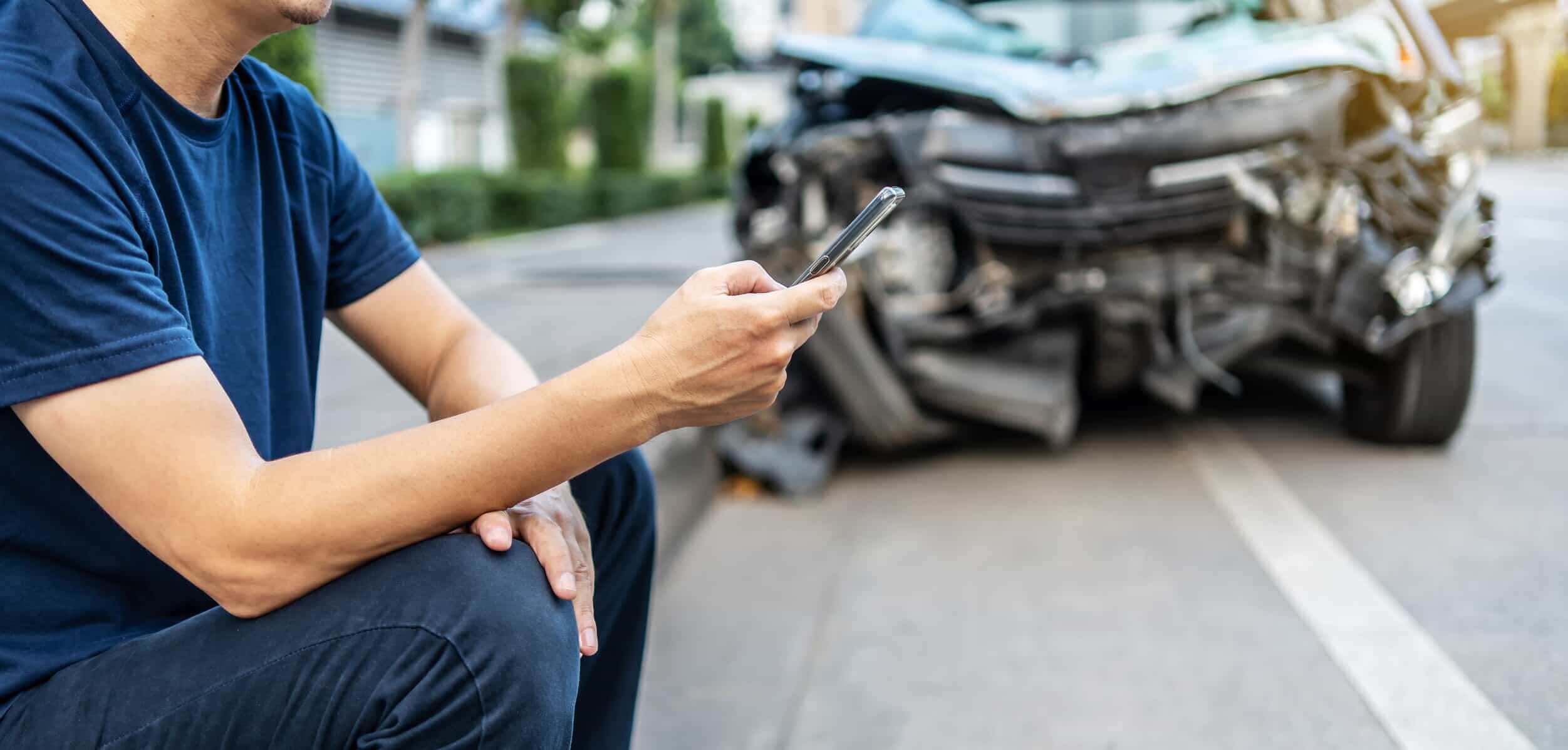
Find essential pain management and auto accident resources that support and promote healing after your injury.
Table of Contents
Introduction
The body may sustain a variety of ailments as a consequence of car accidents. Soft tissue injuries from vehicle accidents are among the most prevalent and may cause severe pain and suffering in many different parts of the body. These injuries can interfere with day-to-day activities and need a systematic approach to pain management. When you have a headache, do you find yourself in a dark, silent room? Do you think your shoulders’ range of motion is limited? Or do you feel ache that radiates down your shoulders and lower back? Guidelines for post-accident pain management are provided in this article, with an emphasis on soft tissue injuries, their symptoms, and available surgical and non-surgical treatment options.
Understanding Soft Tissue Injuries
Soft tissue injuries damage muscles, tendons, ligaments, and fascia. Common examples include whiplash, sprains, strains, and contusions. These injuries frequently occur during automobile accidents due to sudden forces exerted on the body, such as rapid deceleration or impact. The mechanisms of soft tissue injuries can become an issue as they can affect a person’s functionality, especially if the area has overlapping risk profiles. (Arosarena & Eid, 2021)
Symptoms of Soft Tissue Injuries
Various symptoms of soft tissue injuries depend on where the injury is located and how severe it is, but often include:
- Pain and Tenderness: Localized or diffuse pain that worsens with movement or pressure.
- Swelling: Inflammation due to fluid buildup in the affected area.
- Stiffness: Reduced range of motion in joints or muscles.
- Bruising: Discoloration from damaged blood vessels beneath the skin.
- Muscle Spasms: Involuntary contractions causing discomfort.
- Weakness: Reduced strength in the injured area, often noticeable in sprains or strains.
- Neck or Back Pain: Common musculoskeletal pain associated with whiplash, where pain may radiate to the shoulders or arms due to a cracking sound within the cervical spine, causing pain to appear either hours or days. (Bannister et al., 2009)
Beyond the Surface: Understanding the Effects of Personal Injury- Video
Guidelines for Pain Management
Effective pain management after an automobile accident requires a comprehensive approach tailored to the individual’s injury severity, medical history, and response to treatment. The following guidelines provide a framework for managing pain associated with soft tissue injuries.
1. Initial Assessment & Diagnosis
- Medical Evaluation: Individuals should seek immediate medical attention to assess the extent of injuries. A healthcare provider may use physical exams, imaging (e.g., X-rays, MRIs), or diagnostic tests to identify soft tissue damage.
- Pain Assessment: Document pain levels using tools like the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) to guide treatment planning.
- Monitor Symptoms: Track symptoms over time, as some injuries, like whiplash, may have delayed onset.
2. Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatments are typically the first line of management for soft tissue injuries, aiming to reduce pain and inflammation and promote healing.
RICE
- Rest: Limit activities that exacerbate pain to allow tissues to heal.
- Ice: Apply cold packs every fifteen to twenty minutes every hour to reduce swelling and numbness in the affected area. (Hubbard & Denegar, 2004)
- Compression: Use elastic bandages to minimize swelling, ensuring not to wrap too tightly.
- Elevation: Elevating the injured area above the heart level can help reduce fluid buildup.
- Evidence: RICE is widely recommended for acute soft tissue injuries to manage initial symptoms affecting the musculoskeletal system.
Medications
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can temporarily help relieve pain and inflammation in soft tissues.
- Muscle Relaxants: Prescribed for muscle spasms, particularly in whiplash cases.
- Topical Analgesics: Creams or patches for localized pain relief.
- Considerations: Long-term NSAID use should be monitored to avoid gastrointestinal or cardiovascular side effects.
Physical Therapy
- Stretching and Strengthening: Guided exercises to restore mobility and strength.
- Manual Therapy: Massage or myofascial release incorporates various techniques to reduce tension.
- Modalities: Ultrasound, electrical stimulation, or heat therapy to enhance healing. (Papadopoulos & Mani, 2020)
- Evidence: Physical therapy is effective for chronic whiplash and other soft tissue injuries, improving function and reducing pain.
Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture: May reduce pain by stimulating specific points in the body.
- Chiropractic Care: Spinal adjustments to alleviate pain, particularly for neck and back injuries.
- Massage Therapy: Helps promote relaxation and reduces muscle tension where the affected area needs attention.
Acupuncture and chiropractic care show promise for pain relief in soft tissue injuries through various results. Chiropractic care can incorporate soft tissue mobilization to increase internal rotation and improve range of motion by reducing musculoskeletal pain. (Jusdado-García & Cuesta-Barriuso, 2021)
Psychological Support
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps manage chronic pain by addressing emotional and psychological factors.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Reduces stress-related pain amplification.
3. Surgical Treatment Options
Surgery is rarely required for soft tissue injuries; however, they are considered during severe cases or when conservative treatments fail.
Arthroscopic Surgery
They are used to repair or remove damaged tissue from torn ligaments or tendons (e.g., rotator cuff tears). They are minimally invasive, utilizing smaller incisions to reduce persistent pain or instability, creating a faster recovery.
Tendon or Ligament Repair
- Open surgery to reattach or reconstruct severely torn tendons or ligaments is often followed by extensive rehabilitation to restore function.
- Indication: Complete tears causing significant functional impairment.
Fasciotomy
- Rarely used for severe contusions causing compartment syndrome, where pressure buildup threatens tissue viability.
- Involves cutting the fascia to relieve pressure.
- Risks: Infection, scarring, and prolonged recovery.
4. Rehabilitation & Long-Term Management
- Gradual Return to Activity: Follow a structured rehabilitation plan to prevent re-injury.
- Pain Monitoring: Regularly assess pain levels to adjust treatments as needed.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintain a healthy weight, practice good posture, and avoid activities that strain the injured area.
Structured rehabilitation programs improve outcomes for soft tissue injuries by providing multimodal treatments that are customized for the individual. (Bussières et al., 2016)
Considerations & Precautions
- Individualized Care: Treatment plans should account for age, overall health, and injury severity.
- Avoid Overtreatment: Overuse of medications or unnecessary surgeries can lead to complications.
- Follow-Up: Regular check-ups to monitor recovery and address persistent pain.
- Legal and Insurance Aspects: Documents of injuries and treatments for insurance claims or legal proceedings should be related to the accident.
Conclusion
A multimodal strategy is necessary for pain treatment after a car accident, especially for soft tissue injuries such sprains, strains, and whiplash. Combining early medical examination, non-surgical therapies such as RICE, medication, physical therapy, and, in rare instances, surgical intervention may help people achieve successful pain relief and rehabilitation. Getting advice from medical experts and following evidence-based recommendations guarantees the best results.
Injury Medical Chiropractic & Functional Medicine Clinic
We associate certified medical providers who understand the importance of assessing individuals with pain-like symptoms affecting their musculoskeletal system. When asking important questions to our associated medical providers, we advise patients to incorporate customized treatment plans for their pain correlated with musculoskeletal issues after being involved in an auto accident. Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., uses this information as an academic service. Disclaimer
References
Arosarena, O. A., & Eid, I. N. (2021). Mechanisms of Soft Tissue Injury. Facial Plast Surg, 37(4), 424-431. doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1727247
Bannister, G., Amirfeyz, R., Kelley, S., & Gargan, M. (2009). Whiplash injury. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British volume, 91-B(7), 845-850. doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.91b7.22639
Bussières, A. E., Stewart, G., Al-Zoubi, F., Decina, P., Descarreaux, M., Hayden, J., Hendrickson, B., Hincapié, C., Pagé, I., Passmore, S., Srbely, J., Stupar, M., Weisberg, J., & Ornelas, J. (2016). The Treatment of Neck Pain–Associated Disorders and Whiplash-Associated Disorders: A Clinical Practice Guideline. Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics, 39(8), 523-564.e527. doi.org/10.1016/j.jmpt.2016.08.007
Hubbard, T. J., & Denegar, C. R. (2004). Does Cryotherapy Improve Outcomes With Soft Tissue Injury? J Athl Train, 39(3), 278-279. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15496998
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC522152/
Jusdado-García, M., & Cuesta-Barriuso, R. (2021). Soft Tissue Mobilization and Stretching for Shoulder in CrossFitters: A Randomized Pilot Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(2), 575. doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020575
Papadopoulos, E. S., & Mani, R. (2020). The Role of Ultrasound Therapy in the Management of Musculoskeletal Soft Tissue Pain. Int J Low Extrem Wounds, 19(4), 350-358. doi.org/10.1177/1534734620948343
Disclaimer
Disclaimers
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Auto Accident: Your Guide to Healing Through Pain Management" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's wellness blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-C) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on dralexjimenez.com, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card